Page 277 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 277
Organic Chemistry 263
Inorganic compounds: The compounds obtained from nonliving
sources, such as minerals and rocks, were called inorganic compounds.
Organic compounds: The compounds obtained from animals or plants
directly or indirectly were called organic compounds. The chemistry
of such compounds was termed as organic chemistry.
Modern Definition of Organic Chemistry
What is the modern definition of organic compounds
6JG QTICPKE EJGOKUVT[ JCU DGGP TGFGſPGF CU HQNNQYU
“The branch of chemistry which deals with the study of compounds
of carbon with hydrogen (hydrocarbons), and their derivatives is called
organic chemistry.”
Unique (or Versatile) Nature of Carbon
Why is carbon called a versatile element
#DQWV ſXG OKNNKQP EQORQWPFU QH ECTDQP CTG MPQYP *QY FQGU ECTDQP dŚĞ ŵĂŝŶ ƌĞĂƐŽŶ ĨŽƌ ĐĂƌďŽŶ ƚŽ ĨŽƌŵ
make it possible to form such a large number of compounds? The factors ƐƵĐŚ Ă ůĂƌŐĞ ŶƵŵďĞƌ ŽĨ ĐŽŵƉŽƵŶĚƐ
which appear to be responsible for such a unique property of carbon are as ŝƚ ŝƚƐ ƵŶŝƋƵĞ ƉƌŽƉĞƌƚLJ ŽĨ ůŝŶŬŝŶŐ ǁŝƚŚ
follows: ŽƚŚĞƌ ĐĂƌďŽŶ ĂƚŽŵƐ ƚŽ ĨŽƌŵ ůŽŶŐ
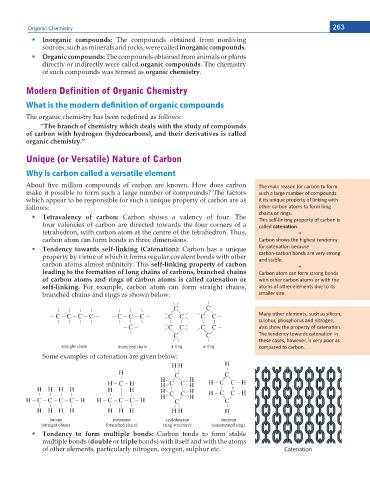
Tetravalency of carbon: Carbon shows a valency of four. The ĐŚĂŝŶƐ Žƌ ƌŝŶŐƐ͘
dŚŝƐ ƐĞůĨͲůŝŶŬŝŶŐ ƉƌŽƉĞƌƚLJ ŽĨ ĐĂƌďŽŶ ŝƐ
four valencies of carbon are directed towards the four corners of a called ĐĂƚĞŶĂƟŽŶ͘
tetrahedron, with carbon atom at the centre of the tetrahedron. Thus, ͻ
carbon atom can form bonds in three dimensions. ĂƌďŽŶ ƐŚŽǁƐ ƚŚĞ ŚŝŐŚĞƐƚ ƚĞŶĚĞŶĐLJ
Tendency towards self-linking (Catenation): Carbon has a unique ĨŽƌ ĐĂƚĞŶĂƟŽŶ ďĞĐĂƵƐĞ
property by virtue of which it forms regular covalent bonds with other ĐĂƌďŽŶͲĐĂƌďŽŶ ďŽŶĚƐ ĂƌĞ ǀĞƌLJ ƐƚƌŽŶŐ
ECTDQP CVQOU CNOQUV KPſPKVGN[ 6JKU self-linking property of carbon ĂŶĚ ƐƚĂďůĞ͘ ͻ
leading to the formation of long chains of carbons, branched chains ĂƌďŽŶ ĂƚŽŵ ĐĂŶ ĨŽƌŵ ƐƚƌŽŶŐ ďŽŶĚƐ
of carbon atoms and rings of carbon atoms is called catenation or ǁŝƚŚ ŽƚŚĞƌ ĐĂƌďŽŶ ĂƚŽŵƐ Žƌ ǁŝƚŚ ƚŚĞ
self-linking. For example, carbon atom can form straight chains, ĂƚŽŵƐ ŽĨ ŽƚŚĞƌ ĞůĞŵĞŶƚƐ ĚƵĞ ƚŽ ŝƚƐ
branched chains and rings as shown below: ƐŵĂůůĞƌ ƐŝnjĞ͘
Many other elements, such as silicon,
sulphur, phosphorus and nitrogen,
ĂůƐŽ ƐŚŽǁ ƚŚĞ ƉƌŽƉĞƌƚLJ ŽĨ ĐĂƚĞŶĂƟŽŶ͘
dŚĞ ƚĞŶĚĞŶĐLJ ƚŽǁĂƌĚƐ ĐĂƚĞŶĂƟŽŶ ŝŶ
ƚŚĞƐĞ ĐĂƐĞƐ͕ ŚŽǁĞǀĞƌ͕ ŝƐ ǀĞƌLJ ƉŽŽƌ ĂƐ
ĐŽŵƉĂƌĞĚ ƚŽ ĐĂƌďŽŶ͘
Some examples of catenation are given below:
Tendency to form multiple bonds: Carbon tends to form stable
multiple bonds (double or triple bonds) with itself and with the atoms
of other elements, particularly nitrogen, oxygen, sulphur etc. Catenation