Page 40 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 40
28 ICSE Chemistry – 10
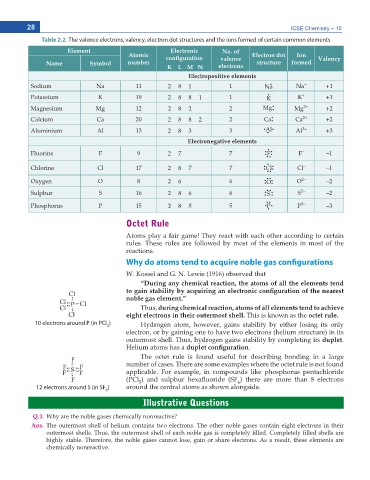
Table 2.2 The valence electrons, valency, electron dot structures and the ions formed of certain common elements
Element Electronic No. of
Atomic EQPſIWTCVKQP valence Electron dot Ion Valency
Name Symbol number structure formed
K L M N electrons
Electropositive elements
Sodium Na 11 2 8 1 1 Na Ŗ Na + +1
Ŗ
Potassium K 19 2 8 8 1 1 K K + +1
Magnesium Mg 12 2 8 2 2 Mg Ŗ Ŗ Mg 2+ +2
Calcium Ca 20 2 8 8 2 2 Ca Ŗ Ŗ Ca 2+ +2
Aluminium Al 13 2 8 3 3 Ŗ Al Ŗ Al 3+ +3
Ŗ
'NGEVTQPGICVKXG GNGOGPVU
Ŗ
Fluorine F 9 2 7 7 Ŗ Ŗ FŖ Ŗ F – –1
Ŗ Ŗ
Ŗ
Chlorine Cl 17 2 8 7 7 Ŗ Ŗ ClŖ Ŗ Cl – –1
Ŗ Ŗ
Ŗ
Oxygen O 8 2 6 6 Ŗ Ŗ OŖ Ŗ Ŗ O 2– –2
Ŗ
Sulphur S 16 2 8 6 6 Ŗ Ŗ S Ŗ Ŗ Ŗ S 2– –2
Phosphorus P 15 2 8 5 5 P Ŗ Ŗ Ŗ Ŗ P 3– –3
Ŗ
Octet Rule
Atoms play a fair game! They react with each other according to certain
rules. These rules are followed by most of the elements in most of the
reactions.
Why do atoms tend to acquire noble gas configurations
W. Kossel and G. N. Lewis (1916) observed that
ő&WTKPI CP[ EJGOKECN TGCEVKQP VJG CVQOU QH CNN VJG GNGOGPVU VGPF
VQ ICKP UVCDKNKV[ D[ CESWKTKPI CP GNGEVTQPKE EQPſIWTCVKQP QH VJG PGCTGUV
PQDNG ICU GNGOGPV Œ
Thus, FWTKPI EJGOKECN TGCEVKQP CVQOU QH CNN GNGOGPVU VGPF VQ CEJKGXG
GKIJV GNGEVTQPU KP VJGKT QWVGTOQUV UJGNN This is known as the octet rule.
10 electrons around P (in PCl ) Hydrogen atom, however, gains stability by either losing its only
5
electron, or by gaining one to have two electrons (helium structure) in its
outermost shell. Thus, hydrogen gains stability by completing its duplet.
Helium atoms has a FWRNGV EQPſIWTCVKQP.
The octet rule is found useful for describing bonding in a large
number of cases. There are some examples where the octet rule is not found
applicable. For example, in compounds like phosphorus pentachloride
(PCl CPF UWNRJWT JGZCƀWQTKFG 5( ) there are more than 8 electrons
5
6
12 electrons around S (in SF ) around the central atoms as shown alongside.
6
Illustrative Questions
Q.1. Why are the noble gases chemically nonreactive?
Ans. The outermost shell of helium contains two electrons. The other noble gases contain eight electrons in their
QWVGTOQUV UJGNNU 6JWU VJG QWVGTOQUV UJGNN QH GCEJ PQDNG ICU KU EQORNGVGN[ ſNNGF %QORNGVGN[ ſNNGF UJGNNU CTG
highly stable. Therefore, the noble gases cannot lose, gain or share electrons. As a result, these elements are
chemically nonreactive.