Page 91 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 91
Study of Acids, Bases and Salts 77
Lead chloride (PbCl ) dissolves in hot water.
2
All sulphates (except sulphates of calcium, lead, barium) are
soluble in water.
All carbonates [except K CO , Na CO , (NH ) CO ] are insoluble
3
2
2
3
3
4 2
in water.
All sulphides (except K S, Na S and (NH ) S) are insoluble in
4 2
2
2
water.
+
+
All oxides and hydroxides (except oxides of Na , K and hydroxides
+
+
of K , and NH ) are insoluble in water.
4
Solubility and nature of solution of some salts in water are given in
Table 3.1.
Table 3.1 Solubility of some salts in water and the nature of their solutions
Soluble/ Nature of salt Soluble/ Nature of salt
Salt Salt
Insoluble solution Insoluble solution
Sodium chloride Soluble Neutral Sodium acetate Soluble Basic
Potassium nitrate Soluble Neutral Sodium carbonate Soluble Basic
Aluminium chloride Soluble Acidic Sodium hydrogencarbonate Soluble Basic
Zinc sulphate Soluble Acidic Lead chloride Insoluble —
Copper sulphate Soluble Acidic Silver chloride Insoluble —
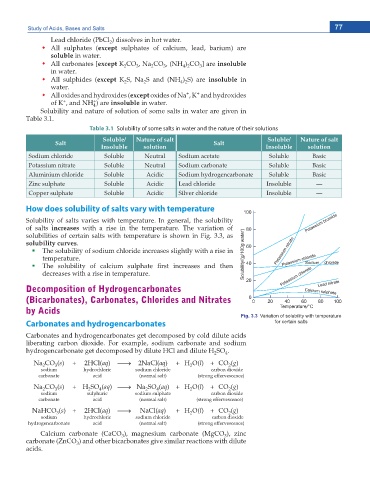
How does solubility of salts vary with temperature
Solubility of salts varies with temperature. In general, the solubility
of salts increases with a rise in the temperature. The variation of
solubilities of certain salts with temperature is shown in Fig. 3.3, as
solubility curves.
The solubility of sodium chloride increases slightly with a rise in
temperature.
6JG UQNWDKNKV[ QH ECNEKWO UWNRJCVG ſTUV KPETGCUGU CPF VJGP
decreases with a rise in temperature.
Decomposition of Hydrogencarbonates
(Bicarbonates), Carbonates, Chlorides and Nitrates
by Acids
Fig. 3.3 Variation of solubility with temperature
Carbonates and hydrogencarbonates for certain salts
Carbonates and hydrogencarbonates get decomposed by cold dilute acids
liberating carbon dioxide. For example, sodium carbonate and sodium
hydrogencarbonate get decomposed by dilute HCl and dilute H SO .
4
2
Na CO (s) + 2HCl(aq) o 2NaCl(aq) + H O(l) + CO (g)
2
3
2
2
sodium hydrochloric sodium chloride carbon dioxide
carbonate acid (normal salt) (strong effervescence)
Na CO (s) + H SO (aq) o Na SO (aq) + H O(l) + CO (g)
4
2
2
4
3
2
2
2
sodium sulphuric sodium sulphate carbon dioxide
carbonate acid (normal salt) (strong effervescence)
NaHCO (s) + 2HCl(aq) o NaCl(aq) + H O(l) + CO (g)
2
2
3
sodium hydrochloric sodium chloride carbon dioxide
hydrogencarbonate acid (normal salt) (strong effervescence)
Calcium carbonate (CaCO ), magnesium carbonate (MgCO ), zinc
3
3
carbonate (ZnCO ) and other bicarbonates give similar reactions with dilute
3
acids.