Page 228 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 228
214 ICSE Chemistry – 10
Experiment to Show that Hydrogen Chloride is
Heavier than Air
Perform the following activity to show that hydrogen chloride gas is
heavier than air:
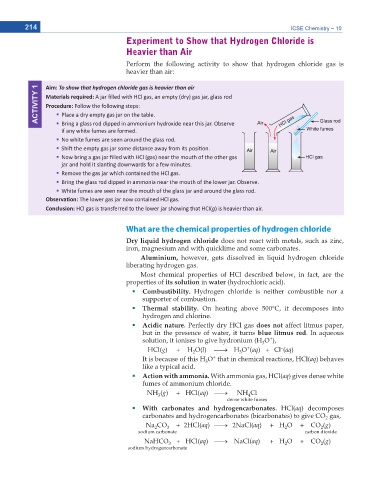
Aim: To show that hydrogen chloride gas is heavier than air
ACTIVITY 1 Materials required: ũĂƌ ĮůůĞĚ ǁŝƚŚ , ů ŐĂƐ͕ ĂŶ ĞŵƉƚLJ ;ĚƌLJͿ ŐĂƐ ũĂƌ͕ ŐůĂƐƐ ƌŽĚ
Procedure: &ŽůůŽǁ ƚŚĞ ĨŽůůŽǁŝŶŐ ƐƚĞƉƐ͗
WůĂĐĞ Ă ĚƌLJ ĞŵƉƚLJ ŐĂƐ ũĂƌ ŽŶ ƚŚĞ ƚĂďůĞ͘
ƌŝŶŐ Ă ŐůĂƐƐ ƌŽĚ ĚŝƉƉĞĚ ŝŶ ĂŵŵŽŶŝƵŵ ŚLJĚƌŽdžŝĚĞ ŶĞĂƌ ƚŚŝƐ ũĂƌ͘ KďƐĞƌǀĞ
ŝĨ ĂŶLJ ǁŚŝƚĞ ĨƵŵĞƐ ĂƌĞ ĨŽƌŵĞĚ͘
EŽ ǁŚŝƚĞ ĨƵŵĞƐ ĂƌĞ ƐĞĞŶ ĂƌŽƵŶĚ ƚŚĞ ŐůĂƐƐ ƌŽĚ͘
^ŚŝŌ ƚŚĞ ĞŵƉƚLJ ŐĂƐ ũĂƌ ƐŽŵĞ ĚŝƐƚĂŶĐĞ ĂǁĂLJ ĨƌŽŵ ŝƚƐ ƉŽƐŝƟŽŶ͘
EŽǁ ďƌŝŶŐ Ă ŐĂƐ ũĂƌ ĮůůĞĚ ǁŝƚŚ , ů ;ŐĂƐͿ ŶĞĂƌ ƚŚĞ ŵŽƵƚŚ ŽĨ ƚŚĞ ŽƚŚĞƌ ŐĂƐ
ũĂƌ ĂŶĚ ŚŽůĚ ŝƚ ƐůĂŶƟŶŐ ĚŽǁŶǁĂƌĚƐ ĨŽƌ Ă ĨĞǁ ŵŝŶƵƚĞƐ͘
ZĞŵŽǀĞ ƚŚĞ ŐĂƐ ũĂƌ ǁŚŝĐŚ ĐŽŶƚĂŝŶĞĚ ƚŚĞ , ů ŐĂƐ͘
ƌŝŶŐ ƚŚĞ ŐůĂƐƐ ƌŽĚ ĚŝƉƉĞĚ ŝŶ ĂŵŵŽŶŝĂ ŶĞĂƌ ƚŚĞ ŵŽƵƚŚ ŽĨ ƚŚĞ ůŽǁĞƌ ũĂƌ͘ KďƐĞƌǀĞ͘
tŚŝƚĞ ĨƵŵĞƐ ĂƌĞ ƐĞĞŶ ŶĞĂƌ ƚŚĞ ŵŽƵƚŚ ŽĨ ƚŚĞ ŐůĂƐƐ ũĂƌ ĂŶĚ ĂƌŽƵŶĚ ƚŚĞ ŐůĂƐƐ ƌŽĚ͘
KďƐĞƌǀĂƟŽŶ͗ dŚĞ ůŽǁĞƌ ŐĂƐ ũĂƌ ŶŽǁ ĐŽŶƚĂŝŶĞĚ , ů ŐĂƐ͘
ŽŶĐůƵƐŝŽŶ͗ , ů ŐĂƐ ŝƐ ƚƌĂŶƐĨĞƌƌĞĚ ƚŽ ƚŚĞ ůŽǁĞƌ ũĂƌ ƐŚŽǁŝŶŐ ƚŚĂƚ , /;gͿ ŝƐ ŚĞĂǀŝĞƌ ƚŚĂŶ Ăŝƌ͘
What are the chemical properties of hydrogen chloride
Dry liquid hydrogen chloride does not react with metals, such as zinc,
iron, magnesium and with quicklime and some carbonates.
Aluminium, however, gets dissolved in liquid hydrogen chloride
liberating hydrogen gas.
Most chemical properties of HCl described below, in fact, are the
properties of its solution in water (hydrochloric acid).
Combustibility. Hydrogen chloride is neither combustible nor a
supporter of combustion.
Thermal stability. On heating above 500°C, it decomposes into
hydrogen and chlorine.
Acidic nature. Perfectly dry HCl gas does not affect litmus paper,
but in the presence of water, it turns blue litmus red. In aqueous
+
solution, it ionises to give hydronium (H O ),
3
+
–
HCl(g) + H O(l) o H O (aq) + Cl (aq)
2
3
+
It is because of this H O that in chemical reactions, HCl(aq) behaves
3
like a typical acid.
Action with ammonia. With ammonia gas, HCl(aq) gives dense white
fumes of ammonium chloride.
NH (g) + HCl(aq) o NH Cl
3
4
dense white fumes
With carbonates and hydrogencarbonates. HCl(aq) decomposes
carbonates and hydrogencarbonates (bicarbonates) to give CO gas,
2
Na CO + 2HCl(aq) o 2NaCl(aq) + H O + CO (g)
2
2
2
3
sodium carbonate carbon dioxide
NaHCO + HCl(aq) o NaCl(aq) + H O + CO (g)
2
3
2
sodium hydrogencarbonate