Page 46 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 46
34 ICSE Chemistry – 10
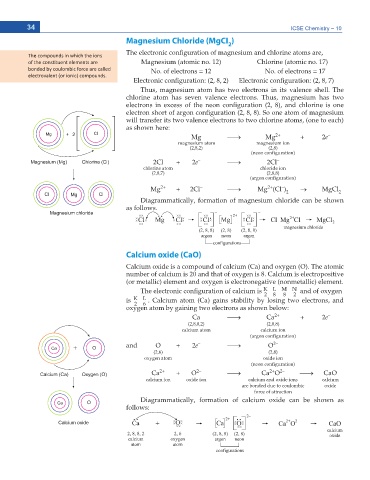
Magnesium Chloride (MgCI )
2
6JG GNGEVTQPKE EQPſIWTCVKQP QH OCIPGUKWO CPF EJNQTKPG CVQOU CTG
dŚĞ ĐŽŵƉŽƵŶĚƐ ŝŶ ǁŚŝĐŚ ƚŚĞ ŝŽŶƐ
ŽĨ ƚŚĞ ĐŽŶƐƟƚƵĞŶƚ ĞůĞŵĞŶƚƐ ĂƌĞ Magnesium (atomic no. 12) Chlorine (atomic no. 17)
ďŽŶĚĞĚ ďLJ ĐŽƵůŽŵďŝĐ ĨŽƌĐĞ ĂƌĞ ĐĂůůĞĚ No. of electrons = 12 No. of electrons = 17
ĞůĞĐƚƌŽǀĂůĞŶƚ ;Žƌ ŝŽŶŝĐͿ ĐŽŵƉŽƵŶĚƐ͘
'NGEVTQPKE EQPſIWTCVKQP 'NGEVTQPKE EQPſIWTCVKQP
Thus, magnesium atom has two electrons in its valence shell. The
chlorine atom has seven valence electrons. Thus, magnesium has two
GNGEVTQPU KP GZEGUU QH VJG PGQP EQPſIWTCVKQP CPF EJNQTKPG KU QPG
GNGEVTQP UJQTV QH CTIQP EQPſIWTCVKQP 5Q QPG CVQO QH OCIPGUKWO
will transfer its two valence electrons to two chlorine atoms, (one to each)
CU UJQYP JGTG
Mg o Mg 2+ + 2e –
magnesium atom magnesium ion
(2,8,2) (2,8)
PGQP EQPſIWTCVKQP
–
2Cl + 2e o 2Cl –
chlorine atom chloride ion
(2,8,7) (2,8,8)
CTIQP EQPſIWTCVKQP
–
–
2+
Mg 2+ + 2Cl o Mg (Cl ) o MgCl 2
2
Diagrammatically, formation of magnesium chloride can be shown
as follows.
Calcium oxide (CaO)
Calcium oxide is a compound of calcium (Ca) and oxygen (O). The atomic
number of calcium is 20 and that of oxygen is 8. Calcium is electropositive
(or metallic) element and oxygen is electronegative (nonmetallic) element.
6JG GNGEVTQPKE EQPſIWTCVKQP QH ECNEKWO KU K L M N and of oxygen
2 8 8 2
is K L . Calcium atom (Ca) gains stability by losing two electrons, and
2 6
QZ[IGP CVQO D[ ICKPKPI VYQ GNGEVTQPU CU UJQYP DGNQY
Ca o Ca 2+ + 2e –
(2,8,8,2) (2,8,8)
calcium atom calcium ion
CTIQP EQPſIWTCVKQP
–
and O + 2e o O 2–
(2,6) (2,8)
oxygen atom oxide ion
PGQP EQPſIWTCVKQP
2+
2–
2–
Ca 2+ + O o Ca O o CaO
calcium ion oxide ion calcium and oxide ions calcium
are bonded due to coulombic oxide
force of attraction
Diagrammatically, formation of calcium oxide can be shown as
HQNNQYU