Page 50 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 50
38 ICSE Chemistry – 10
What is a covalent bond
The bond formed due to mutual sharing of electrons by the combining
atoms is called covalent bond.
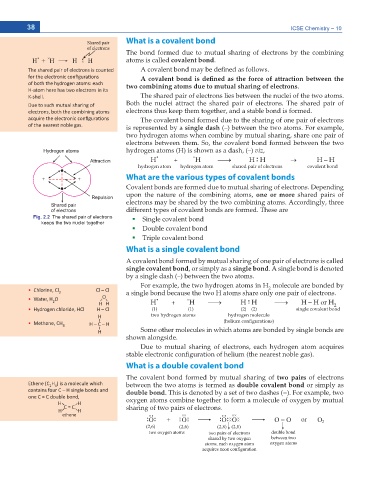
dŚĞ ƐŚĂƌĞĚ ƉĂŝƌ ŽĨ ĞůĞĐƚƌŽŶƐ ŝƐ ĐŽƵŶƚĞĚ # EQXCNGPV DQPF OC[ DG FGſPGF CU HQNNQYU
ĨŽƌ ƚŚĞ ĞůĞĐƚƌŽŶŝĐ ĐŽŶĮŐƵƌĂƟŽŶƐ # EQXCNGPV DQPF KU FGſPGF CU VJG HQTEG QH CVVTCEVKQP DGVYGGP VJG
ŽĨ ďŽƚŚ ƚŚĞ ŚLJĚƌŽŐĞŶ ĂƚŽŵƐ͗ ĞĂĐŚ VYQ EQODKPKPI CVQOU FWG VQ OWVWCN UJCTKPI QH GNGEVTQPU.
,ͲĂƚŽŵ ŚĞƌĞ ŚĂƐ ƚǁŽ ĞůĞĐƚƌŽŶƐ ŝŶ ŝƚƐ
<ͲƐŚĞůů͘ The shared pair of electrons lies between the nuclei of the two atoms.
Both the nuclei attract the shared pair of electrons. The shared pair of
ƵĞ ƚŽ ƐƵĐŚ ŵƵƚƵĂů ƐŚĂƌŝŶŐ ŽĨ
ĞůĞĐƚƌŽŶƐ͕ ďŽƚŚ ƚŚĞ ĐŽŵďŝŶŝŶŐ ĂƚŽŵƐ electrons thus keep them together, and a stable bond is formed.
ĂĐƋƵŝƌĞ ƚŚĞ ĞůĞĐƚƌŽŶŝĐ ĐŽŶĮŐƵƌĂƟŽŶƐ The covalent bond formed due to the sharing of one pair of electrons
ŽĨ ƚŚĞ ŶĞĂƌĞƐƚ ŶŽďůĞ ŐĂƐ͘ is represented by a UKPING FCUJ (–) between the two atoms. For example,
two hydrogen atoms when combine by mutual sharing, share one pair of
electrons between them. So, the covalent bond formed between the two
hydrogen atoms (H) is shown as a dash, (–) viz,
H Ŗ + × H o HH o H – H
Ŗ
×
hydrogen atom hydrogen atom shared pair of electrons covalent bond
What are the various types of covalent bonds
Covalent bonds are formed due to mutual sharing of electrons. Depending
upon the nature of the combining atoms, one or more shared pairs of
electrons may be shared by the two combining atoms. Accordingly, three
different types of covalent bonds are formed. These are
Fig. 2.2 The shared pair of electrons Single covalent bond
keeps the two nuclei together
Double covalent bond
Triple covalent bond
What is a single covalent bond
A covalent bond formed by mutual sharing of one pair of electrons is called
UKPING EQXCNGPV DQPF, or simply as a UKPING DQPF. A single bond is denoted
by a single dash (–) between the two atoms.
For example, the two hydrogen atoms in H molecule are bonded by
ͻഩ ŚůŽƌŝŶĞ͕ ů ů ʹ ů 2
Ϯ a single bond because the two H atoms share only one pair of electrons.
ͻഩtĂƚĞƌ͕ , K – O – Ŗ ×
Ŗ
Ϯ H + H o HH o H – H or H
×
, , 2
ͻഩ,LJĚƌŽŐĞŶ ĐŚůŽƌŝĚĞ͕ , ů , ʹ ů (1) (1) (2) (2) single covalent bond
– , two hydrogen atoms hydrogen molecule
ͻഩDĞƚŚĂŶĞ͕ , JGNKWO EQPſIWTCVKQPU
ϰ , ʹ ʹ ,
– Some other molecules in which atoms are bonded by single bonds are
,
shown alongside.
Due to mutual sharing of electrons, each hydrogen atom acquires
UVCDNG GNGEVTQPKE EQPſIWTCVKQP QH JGNKWO VJG PGCTGUV PQDNG ICU
What is a double covalent bond
The covalent bond formed by mutual sharing of two pairs of electrons
ƚŚĞŶĞ ; , Ϳ ŝƐ Ă ŵŽůĞĐƵůĞ ǁŚŝĐŚ between the two atoms is termed as double covalent bond or simply as
Ϯ ϰ
ĐŽŶƚĂŝŶƐ ĨŽƵƌ ʹ , ƐŝŶŐůĞ ďŽŶĚƐ ĂŶĚ double bond. This is denoted by a set of two dashes (=). For example, two
ŽŶĞ с ĚŽƵďůĞ ďŽŶĚ͕ oxygen atoms combine together to form a molecule of oxygen by mutual
– , – ,
– с sharing of two pairs of electrons.
, – ,
ĞƚŚĞŶĞ