Page 55 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 55
Chemical Bonding 43
e.g., HCl, in water conduct electricity due to the presence of ions in its
solution.
HCl(g) + H O(l) o H O + + Cl –
2 3
The solution becomes conducting due to these ions in the solution.
Thermal conductivity. Covalent compounds have very low thermal
conductivities. Diamond and graphite have very high thermal
conductivity.
Solubility. Covalent compounds are usually insoluble in polar
solvents like water. The covalent compounds, however, dissolve in ŽǀĂůĞŶƚ ĐŽŵƉŽƵŶĚƐ ƐŚŽǁ
nonpolar solvents, like benzene, toluene, etc. ŝƐŽŵĞƌŝƐŵ͘
Slow rate of reaction. The reactions of the covalent compounds are
quite slow. This is because the covalent compounds take part in
reactions as, molecules, and the molecular reactions are slow.
Isomerism. Covalent bonds are rigid and directional. Therefore,
these can give different arrangements of atoms in space. So, a single
molecular formula may represent a number of different compounds
with different properties. This phenomenon is called isomerism.
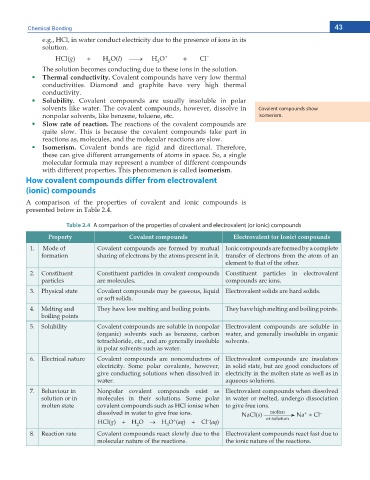
How covalent compounds differ from electrovalent
(ionic) compounds
A comparison of the properties of covalent and ionic compounds is
presented below in Table 2.4.
Table 2.4 A comparison of the properties of covalent and electrovalent (or ionic) compounds
Property Covalent compounds Electrovalent (or Ionic) compounds
1. Mode of Covalent compounds are formed by mutual Ionic compounds are formed by a complete
formation sharing of electrons by the atoms present in it. transfer of electrons from the atom of an
element to that of the other.
2. Constituent Constituent particles in covalent compounds Constituent particles in electrovalent
particles are molecules. compounds are ions.
3. Physical state Covalent compounds may be gaseous, liquid Electrovalent solids are hard solids.
or soft solids.
4. Melting and They have low melting and boiling points. They have high melting and boiling points.
boiling points
5. Solubility Covalent compounds are soluble in nonpolar Electrovalent compounds are soluble in
(organic) solvents such as benzene, carbon water, and generally insoluble in organic
tetrachloride, etc., and are generally insoluble solvents.
in polar solvents such as water.
6. Electrical nature Covalent compounds are nonconductors of Electrovalent compounds are insulators
electricity. Some polar covalents, however, in solid state, but are good conductors of
give conducting solutions when dissolved in electricity in the molten state as well as in
water. aqueous solutions.
7. Behaviour in Nonpolar covalent compounds exist as Electrovalent compounds when dissolved
solution or in molecules in their solutions. Some polar in water or melted, undergo dissociation
molten state covalent compounds such as HCl ionise when to give free ions.
dissolved in water to give free ions. NaCl(s) molten Na + Cl –
+
+
–
HCl(g) + H O o H O (aq) + Cl (aq) or solution
2 3
8. Reaction rate Covalent compounds react slowly due to the Electrovalent compounds react fast due to
molecular nature of the reactions. the ionic nature of the reactions.