Page 164 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 164
152 ICSE Chemistry – 9
boiling
Zn(s) + 2NaOH(aq) o NaZnO (aq) + H (g)
2
2
zinc (powder) sodium hydroxide sodium zincate hydrogen
boiling
2Al(s) + 2NaOH(aq) + 2H O(l) o 2NaAlO (aq) + 3H (g)
2
2
2
aluminium sodium aluminate hydrogen
(powder)
boiling
Sn(s) + 2NaOH(aq) + H O(l) o Na SnO (aq) + 2H (g)
2
3
2
2
tin sodium stannate hydrogen
boiling
Si(s) + 2NaOH(aq) + H O(l) o Na SiO 3 + 2H (g)
2
2
2
silicon sodium silicate hydrogen
'
Pb(s) + NaOH + 2H O o Na[Pb(OH) ] + H (g)
2
3
2
lead sodium plumbite hydrogen
Action of KOH on Al, Zn, Pb
2Al + 2KOH + 6H O o 2K[Al(OH) ] + 3H (g)
4
2
2
aluminium potassium hydroxide potassium aluminate hydrogen
Zn + 2KOH + 2H O o K [Zn(OH) ] + H (g)
4
2
2
2
zinc potassium hydroxide potassium hydrogen
zincate
Pb + 2KOH + 2H O o K [Pb(OH) ] + H (g)
2
4
2
2
lead potassium hydroxide potassium hydrogen
plumbate
Laboratory Preparation of Hydrogen
How is hydrogen prepared in the laboratory
In laboratory, hydrogen gas is generally prepared by the action of dilute
H SO on zinc metal (in the form of small granules).
2
4
Reaction : Zn(s) + H SO (aq) o ZnSO (aq) + H (g)
2
4
2
4
zinc hydrogen
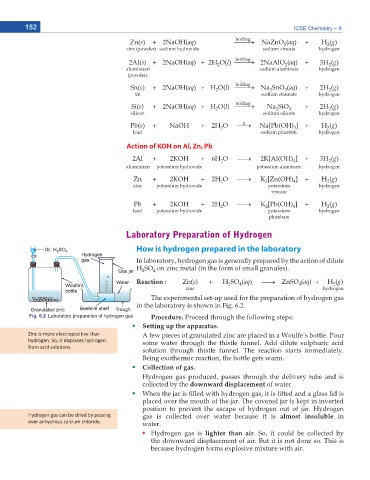
The experimental set-up used for the preparation of hydrogen gas
in the laboratory is shown in Fig. 6.2.
Fig. 6.2 Laboratory preparation of hydrogen gas 2TQEGFWTG Proceed through the following steps:
Setting up the apparatus.
ŝŶĐ ŝƐ ŵŽƌĞ ĞůĞĐƚƌŽƉŽƐŝƟǀĞ ƚŚĂŶ A few pieces of granulated zinc are placed in a Woulfe’s bottle. Pour
ŚLJĚƌŽŐĞŶ͘ ^Ž͕ ŝƚ ĚŝƐƉůĂĐĞƐ ŚLJĚƌŽŐĞŶ some water through the thistle funnel. Add dilute sulphuric acid
ĨƌŽŵ ĂĐŝĚ ƐŽůƵƟŽŶƐ͘
solution through thistle funnel. The reaction starts immediately.
Being exothermic reaction, the bottle gets warm.
%QNNGEVKQP QH ICU
Hydrogen gas produced, passes through the delivery tube and is
collected by the downward displacement of water.
When the jar is lled with hydrogen gas, it is lifted and a glass lid is
placed over the mouth of the jar. The covered jar is kept in inverted
position to prevent the escape of hydrogen out of jar. Hydrogen
,LJĚƌŽŐĞŶ ŐĂƐ ĐĂŶ ďĞ ĚƌŝĞĚ ďLJ ƉĂƐƐŝŶŐ gas is collected over water because it is almost insoluble in
ŽǀĞƌ ĂŶŚLJĚƌŽƵƐ ĐĂůĐŝƵŵ ĐŚůŽƌŝĚĞ͘ water.
Hydrogen gas is lighter than air. So, it could be collected by
the downward displacement of air. But it is not done so. This is
because hydrogen forms explosive mixture with air.