Page 165 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 165
Study of the First Element : Hydrogen 153
Manufacture of Hydrogen Gas ^ŽŵĞ ĐŽŵŵŽŶůLJ ĨŽƵŶĚ ŝŵƉƵƌŝƟĞƐ
ŝŶ ŚLJĚƌŽŐĞŶ ŐĂƐ ĂŶĚ ƚŚĞŝƌ ƌĞŵŽǀĂů ŝƐ
How is hydrogen manufactured ĚĞƐĐƌŝďĞĚ ďĞůŽǁ͗
Water is one of the most abundant and cheaper source of hydrogen. ͻഩ SO , CO and NO
2
2
2
LJ ƉĂƐƐŝŶŐ ƚŚƌŽƵŐŚ ĐŽŶĐ͘ ƐŽůƵƟŽŶ
Hydrogen is commercially obtained from water using different methods. ŽĨ <K,͘
Some of them are described here. ͻഩ H S gas
2
LJ ƉĂƐƐŝŶŐ ƚŚƌŽƵŐŚ ůĞĂĚ ŶŝƚƌĂƚĞ
From water gas: Bosch process ƐŽůƵƟŽŶ
ͻഩ Nitrogen gas
The largest amount of commercial hydrogen is manufactured from water LJ ƉĂƐƐŝŶŐ ƚŚĞ ŐĂƐ ŽǀĞƌ ƉĂůůĂĚŝƵŵ
gas. This process consists of three steps: ĨŽŝů͕ ĂŶĚ ƌĞĐŽǀĞƌŝŶŐ ŚLJĚƌŽŐĞŶ ŐĂƐ
Step 1: Steam is passed through a mass of red hot coke (>1000°C). A mixture of ďLJ ŚĞĂƟŶŐ ƉĂůůĂĚŝƵŵ ĨŽŝů ŝŶ ĂŶ
equal volumes of hydrogen and carbon monoxide, known as water gas, ĞǀĂĐƵĂƚĞĚ ǀĞƐƐĞů͘
is formed.
'
C(s) + H O(g) o CO(g) + H (g)
2
2
red hot steam water gas
Step 2: Water gas is mixed with excess of steam and passed over a heated
catalyst, ferric oxide and little chromium oxide at 450°C. Carbon
monoxide is oxidised to CO .
2
Fe O + Cr O
CO(g) + H O(g) o CO (g) + H (g)
3
2
2
3
2
2
2
from water gas steam 450°C
Step 3: The mixture of CO and H is passed through water under a pressure
2
2
of 25 – 30 atm, when CO gets dissolved in water and hydrogen gas is
2
collected.
under
H O(l) + H (g) + CO (g) o H CO (aq) + H (g)
2
2
3
2
2
2
pressure
carbon dioxide
dissolves in water
Removal of CO and CO Water gas is an equimolar mixture
2
of CO and H . CO is oxidised to CO , and CO is removed by
2
2
2
dissolving in water under pressure. Thus, hydrogen obtained is
free from both CO and CO .
2
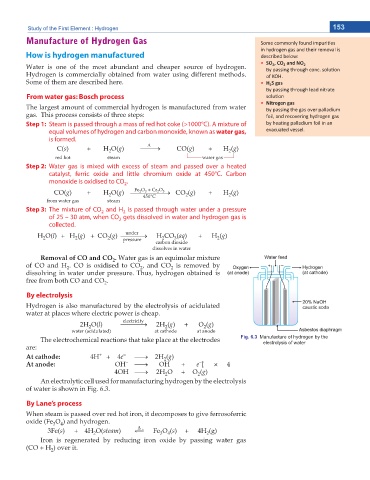
By electrolysis
Hydrogen is also manufactured by the electrolysis of acidulated
water at places where electric power is cheap.
electricity
2H O(l) o 2H (g) + O (g)
2
2
2
water (acidulated) at cathode at anode
The electrochemical reactions that take place at the electrodes Fig. 6.3 Manufacture of hydrogen by the
electrolysis of water
are:
+
–
At cathode: 4H + 4e o 2H (g)
2
–
–
At anode: OH o OH + e ] × 4
4OH o 2H O + O (g)
2
2
An electrolytic cell used for manufacturing hydrogen by the electrolysis
of water is shown in Fig. 6.3.
By Lane’s process
When steam is passed over red hot iron, it decomposes to give ferrosoferric
oxide (Fe O ) and hydrogen.
3
4
3Fe(s) + 4H O(steam) Fe O (s) + 4H (g)
3
2
2
4
Iron is regenerated by reducing iron oxide by passing water gas
(CO + H ) over it.
2