Page 189 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 189
Study of Gas Laws 177
Therefore,
–3
101325 × (22.414 × 10 )
–1
R = N m mol K –1
273.15
–1
= 8.314 J mol K –1
The value of the universal gas constant (R) in SI units is
–1
–1
8.314 J mol K .
Values of the universal gas constant (R) in different units are recorded
below:
Table 7.1. Values of universal gas constant (R) in different units
Unit R Unit R
–1
–1
L atm K mol –1 0.0821 erg K mol –1 8.3 × 10 7
–1
–1
mL atm K mol –1 82.1 cal K mol –1 1.987
–1
–1
L Torr K mol –1 62.4 J K mol –1 8.31
How to obtain the actual pressure exerted by a gas
collected over water
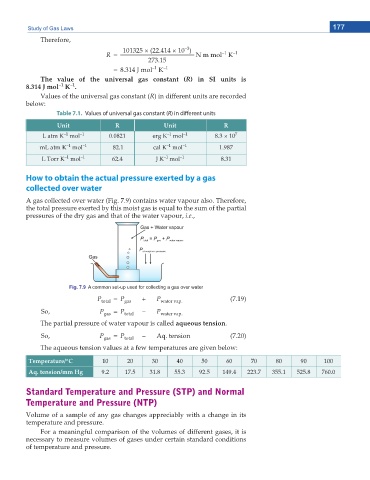
A gas collected over water (Fig. 7.9) contains water vapour also. Therefore,
the total pressure exerted by this moist gas is equal to the sum of the partial
pressures of the dry gas and that of the water vapour, i.e.,
Fig. 7.9 A common set-up used for collecting a gas over water
P total = P gas + P water vap. (7.19)
So, P gas = P total – P water vap.
The partial pressure of water vapour is called aqueous tension.
So, P gas = P total – Aq. tension (7.20)
The aqueous tension values at a few temperatures are given below:
Temperature/°C 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Aq. tension/mm Hg 9.2 17.5 31.8 55.3 92.5 149.4 223.7 355.1 525.8 760.0
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) and Normal
Temperature and Pressure (NTP)
Volume of a sample of any gas changes appreciably with a change in its
temperature and pressure.
For a meaningful comparison of the volumes of different gases, it is
necessary to measure volumes of gases under certain standard conditions
of temperature and pressure.