Page 185 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 185
Study of Gas Laws 173
(ii) V = 400 mL
1
V = 1 × V = 200 mL
2
1
2
T = 290.15 K
1
T = ?
2
V × T 200 mL × 290.15 K
T = 2 1 = = 145.07 K
2
V 1 400 mL
or t = (145.07 – 273.15)°C = – 128.08°C
2
Charles’ Law and the Absolute (Kelvin)
Temperature Scale
How is the absolute temperature scale derived from the
Charles’ law
Charles observed that the volume of certain amount of a gas changes by
V /273.15 for each degree rise or fall in temperature. V being the volume at
0
0
0°C. The volume of the gas at any temperature t °C is given by,
⎛ t (C)° ⎞
V = V 1+ 273.15 ⎠ ⎟
0 ⎜
t
⎝
Now, if the temperature is lowered, it becomes clear that at
t = – 273.15°C, the volume of the gas becomes zero.
⎛ − 273.15 ⎞
V = V 1+ 273.15 ⎠ 0
⎟ = V (1 – 1) = 0
0 ⎜
⎝
t
Below t = – 273.15°C, the V becomes negative. Such a situation
t
is absurd. Therefore, the physically signi cant lowest temperature is
– 273.15°C.
The lowest temperature of – 273.15°C, at which gas ceases to exist or at
which volume of any gas becomes zero is called absolute zero.
The temperature scale based on the absolute zero as its starting point
is known as the absolute scale or the Kelvin scale of temperature.
On this scale, temperatures are expressed as,
T (K) = t°C + 273.15 (7.10)
The size of the degree is equal on both the Celsius and Kelvin scales.
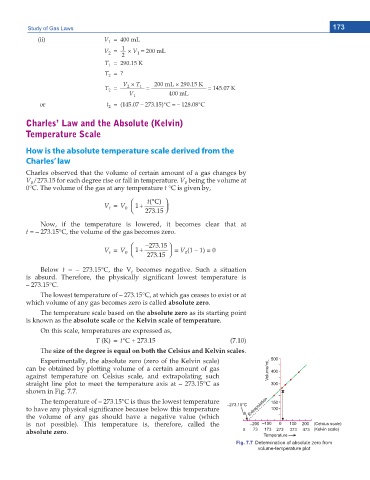
Experimentally, the absolute zero (zero of the Kelvin scale)
can be obtained by plotting volume of a certain amount of gas
against temperature on Celsius scale, and extrapolating such
straight line plot to meet the temperature axis at – 273.15°C as
shown in Fig. 7.7.
The temperature of – 273.15°C is thus the lowest temperature
to have any physical signi cance because below this temperature
the volume of any gas should have a negative value (which
is not possible). This temperature is, therefore, called the
absolute zero.
Fig. 7.7 Determination of absolute zero from
volume-temperature plot