Page 30 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 30
18 ICSE Chemistry – 9
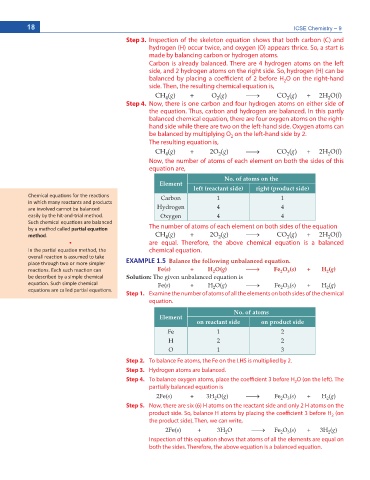
Step 3. Inspection of the skeleton equation shows that both carbon (C) and
hydrogen (H) occur twice, and oxygen (O) appears thrice. So, a start is
made by balancing carbon or hydrogen atoms.
Carbon is already balanced. There are 4 hydrogen atoms on the left
side, and 2 hydrogen atoms on the right side. So, hydrogen (H) can be
balanced by placing a coefficient of 2 before H O on the right-hand
2
side. Then, the resulting chemical equation is,
CH (I) + O (I) o CO (I) + 2H O(N)
2
2
2
4
Step 4. Now, there is one carbon and four hydrogen atoms on either side of
the equation. Thus, carbon and hydrogen are balanced. In this partly
balanced chemical equation, there are four oxygen atoms on the right-
hand side while there are two on the left-hand side. Oxygen atoms can
be balanced by multiplying O on the left-hand side by 2.
2
The resulting equation is,
CH (I) + 2O (I) o CO (I) + 2H O(N)
2
2
2
4
Now, the number of atoms of each element on both the sides of this
equation are,
No. of atoms on the
Element
left (reactant side) right (product side)
ŚĞŵŝĐĂů ĞƋƵĂƟŽŶƐ ĨŽƌ ƚŚĞ ƌĞĂĐƟŽŶƐ Carbon 1 1
ŝŶ ǁŚŝĐŚ ŵĂŶLJ ƌĞĂĐƚĂŶƚƐ ĂŶĚ ƉƌŽĚƵĐƚƐ
ĂƌĞ ŝŶǀŽůǀĞĚ ĐĂŶŶŽƚ ďĞ ďĂůĂŶĐĞĚ Hydrogen 4 4
ĞĂƐŝůLJ ďLJ ƚŚĞ ŚŝƚͲĂŶĚͲƚƌŝĂů ŵĞƚŚŽĚ͘ Oxygen 4 4
^ƵĐŚ ĐŚĞŵŝĐĂů ĞƋƵĂƟŽŶƐ ĂƌĞ ďĂůĂŶĐĞĚ
ďLJ Ă ŵĞƚŚŽĚ ĐĂůůĞĚ ƉĂƌƟĂů ĞƋƵĂƟŽŶ The number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation
ŵĞƚŚŽĚ͘ CH (I) + 2O (I) o CO (I) + 2H O(N)
4
2
2
2
ͻ are equal. Therefore, the above chemical equation is a balanced
/Ŷ ƚŚĞ ƉĂƌƟĂů ĞƋƵĂƟŽŶ ŵĞƚŚŽĚ͕ ƚŚĞ chemical equation.
ŽǀĞƌĂůů ƌĞĂĐƟŽŶ ŝƐ ĂƐƐƵŵĞĚ ƚŽ ƚĂŬĞ
ƉůĂĐĞ ƚŚƌŽƵŐŚ ƚǁŽ Žƌ ŵŽƌĞ ƐŝŵƉůĞƌ EXAMPLE 1.5 Balance the following unbalanced equation.
ƌĞĂĐƟŽŶƐ͘ ĂĐŚ ƐƵĐŚ ƌĞĂĐƟŽŶ ĐĂŶ Fe(s) + H O(g) o Fe O (s) + H (g)
2
2
3
2
ďĞ ĚĞƐĐƌŝďĞĚ ďLJ Ă ƐŝŵƉůĞ ĐŚĞŵŝĐĂů Solution: The given unbalanced equation is
ĞƋƵĂƟŽŶ͘ ^ƵĐŚ ƐŝŵƉůĞ ĐŚĞŵŝĐĂů Fe(U) + H O(I) o Fe O (U) + H (I)
ĞƋƵĂƟŽŶƐ ĂƌĞ ĐĂůůĞĚ ƉĂƌƟĂů ĞƋƵĂƟŽŶƐ͘ 2 2 3 2
Step 1. Examine the number of atoms of all the elements on both sides of the chemical
equation.
No. of atoms
Element
on reactant side on product side
Fe 1 2
H 2 2
O 1 3
Step 2. To balance Fe atoms, the Fe on the LHS is multiplied by 2.
Step 3. Hydrogen atoms are balanced.
Step 4. To balance oxygen atoms, place the coefficient 3 before H O (on the left). The
2
partially balanced equation is
2Fe(U) + 3H O(I) o Fe O (U) + H (I)
2
2
2
3
Step 5. Now, there are six (6) H atoms on the reactant side and only 2 H atoms on the
product side. So, balance H atoms by placing the coefficient 3 before H (on
2
the product side). Then, we can write,
2Fe(U) + 3H O o Fe O (U) + 3H (I)
2
3
2
2
Inspection of this equation shows that atoms of all the elements are equal on
both the sides. Therefore, the above equation is a balanced equation.