Page 110 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 110
96 ICSE Chemistry – 10
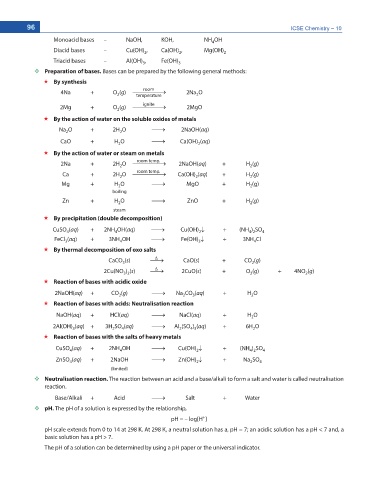
Monoacid bases – NaOH, KOH, NH OH
4
Diacid bases – Cu(OH) , Ca(OH) , Mg(OH)
2 2 2
Triacid bases – Al(OH) , Fe(OH)
3 3
Preparation of bases. Bases can be prepared by the following general methods:
By synthesis
room
4Na + O (g) o 2Na O
2
2
temperature
ignite
2Mg + O (g) o 2MgO
2
By the action of water on the soluble oxides of metals
Na O + 2H O o 2NaOH(aq)
2
2
CaO + H O o Ca(OH) (aq)
2 2
By the action of water or steam on metals
room temp.
2Na + 2H O o 2NaOH(aq) + H (g)
2 2
room temp.
Ca + 2H O o Ca(OH) (aq) + H (g)
2
2
2
Mg + H O o MgO + H (g)
2
2
boiling
Zn + H O o ZnO + H (g)
2 2
steam
By precipitation (double decomposition)
CuSO (aq) + 2NH OH(aq) o Cu(OH) p + (NH ) SO 4
4
4
2
4 2
FeCl (aq) + 3NH OH o Fe(OH) p + 3NH Cl
3
3
4
4
By thermal decomposition of oxo salts
'
CaCO (s) o CaO(s) + CO (g)
3
2
'
2Cu(NO ) (s) o 2CuO(s) + O (g) + 4NO (g)
3 2
2
2
Reaction of bases with acidic oxide
2NaOH(aq) + CO (g) o Na CO (aq) + H O
2
2
2
3
Reaction of bases with acids: Neutralisation reaction
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) o NaCl(aq) + H O
2
2Al(OH) (aq) + 3H SO (aq) o Al (SO ) (aq) + 6H O
4
4 3
2
2
3
2
Reaction of bases with the salts of heavy metals
CuSO (aq) + 2NH OH o Cu(OH) p + (NH ) SO 4
4 2
4
4
2
ZnSO (aq) + 2NaOH o Zn(OH) p + Na SO
4 2 2 4
(limited)
Neutralisation reaction. The reaction between an acid and a base/alkali to form a salt and water is called neutralisation
reaction.
Base/Alkali + Acid o Salt + Water
pH. The pH of a solution is expressed by the relationship,
+
pH = – log[H ]
pH scale extends from 0 to 14 at 298 K. At 298 K, a neutral solution has a, pH = 7; an acidic solution has a pH < 7 and, a
basic solution has a pH > 7.
The pH of a solution can be determined by using a pH paper or the universal indicator.