Page 22 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 22
10 ICSE Chemistry – 10
First ionisation energy < Second ionisation energy < Third ionisation energy
K G I < I < I 3
2
1
First, second and third ionisation energies of a few typical elements
are given below:
Atomic Ionisation energy (kJ/mol)
Element
number First Second Third
Na 11 495 4565 6916
Mg 12 736 1443 7690
Al 13 577 1833 2745
On what factors does the ionisation energy of an element
depend
The magnitude of the ionisation energy of an element depends mainly
upon the following factors:
Size of the atom or ion. The ionisation energy depends upon the
coulombic force of attraction between the nucleus and the outermost
GNGEVTQPU 6JKU EQWNQODKE HQTEG QH CVVTCEVKQP FGETGCUGU YJGP VJG
FKUVCPEG DGVYGGP VJG PWENGWU CPF GNGEVTQPU KPETGCUGU +P DKIIGT
atoms, the outermost electrons are at greater distance than in the
UOCNNGT CVQOU 5Q VJG HQTEG QH CVVTCEVKQP DGVYGGP VJG PWENGWU CPF VJG
QWVGTOQUV GNGEVTQPU KU YGCMGT KP DKIIGT CVQOU KQPU 6JGTGHQTG VJG
ionisation energy decreases as the size of the atom increases and
vice-versa
Nuclear charge. The strength of the attractive forces between the
dŚĞƌĞ ĂƌĞ ƐŽŵĞ ŽƚŚĞƌ ĨĂĐƚŽƌƐ ƚŚĂƚ
ĂīĞĐƚ ƚŚĞ ŝŽŶŝƐĂƟŽŶ ĞŶĞƌŐLJ ŽĨ ĂŶ PWENGWU CPF VJG GNGEVTQPU FGRGPFU WRQP VJG PWENGCT EJCTIG )TGCVGT
ĞůĞŵĞŶƚ͘ dŚĞƐĞ ǁŝůů ďĞ ƚĂƵŐŚƚ ƚŽ LJŽƵ the effective nuclear charge, greater is the electrostatic force of
ŝŶ LJŽƵƌ ŚŝŐŚĞƌ ĐůĂƐƐĞƐ͘ CVVTCEVKQP DGVYGGP VJG PWENGWU CPF VJG GNGEVTQPU 6JKU OCMGU VJG
TGOQXCN QH CP GNGEVTQP HTQO VJG CVQO QT KQP OQTG FKHſEWNV #U C
result, ionisation energy increases with an increase in the effective
nuclear charge
Periodic Variation of Ionisation Energy
Ionisation energy of an element depends upon the strength with
YJKEJ VJG GNGEVTQP VQ DG TGOQXGF KU DQWPF VQ VJG PWENGWU 6JWU VJG
ionisation energy of an element depends upon its location in the
RGTKQFKE VCDNG
How does ionisation energy vary in a group
The ionisation energy decreases in going from top to the bottom in a
ITQWR 6JG ſTUV KQPKUCVKQP XCNWGU QH CNMCNK OGVCNU CTG IKXGP DGNQY CPF
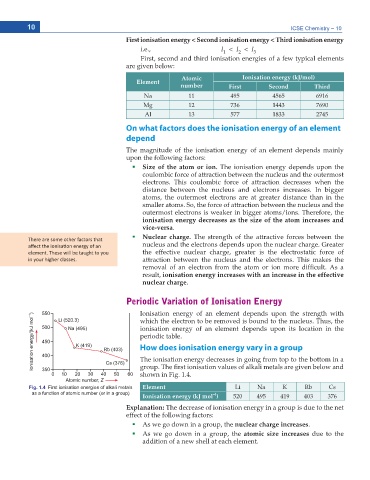
UJQYP KP (KI
Fig. 1.4 First ionisation energies of alkali metals Element Li Na K Rb Cs
as a function of atomic number (or in a group) –l
Ionisation energy (kJ mol ) 520 495 419 403 376
Explanation: The decrease of ionisation energy in a group is due to the net
effect of the following factors:
As we go down in a group, the nuclear charge increases
As we go down in a group, the atomic size increases due to the
CFFKVKQP QH C PGY UJGNN CV GCEJ GNGOGPV