Page 17 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 17
Periodic Properties and Variations of Properties (Physical and Chemical) 5
On what factors does the atomic size of an element dŚĞ ĂƚŽŵŝĐ ƐŝnjĞ ŵĂLJ ďĞ ĞdžƉƌĞƐƐĞĚ ŝŶ
depend ƚĞƌŵƐ ŽĨ ĞŝƚŚĞƌ ŽĨ ƚŚĞ ĨŽůůŽǁŝŶŐ ƌĂĚŝŝ͗
ͻഩĐŽǀĂůĞŶƚ ƌĂĚŝƵƐ
The atomic size of an element depends on the following two factors: ͻഩǀĂŶ ĚĞƌ tĂĂůƐ͛ ƌĂĚŝƵƐ
Number of electronic shells and ͻഩŵĞƚĂůůŝĐ ;Žƌ ĐƌLJƐƚĂůͿ ƌĂĚŝƵƐ
Ƶƚ ŐĞŶĞƌĂůůLJ ƚŚĞ ĐŽǀĂůĞŶƚ ƌĂĚŝŝ ĂƌĞ
Nuclear charge (or the number of protons) ƵƐĞĚ ĨŽƌ ĚĞƐĐƌŝďŝŶŐ ƚŚĞ ĂƚŽŵŝĐ ƐŝnjĞƐ͘
Number of electronic shells. The size of the atom of an element increases /Ŷ ƚŚĞ ĐĂƐĞ ŽĨ ŶŽďůĞ ŐĂƐĞƐ͕ ŚŽǁĞǀĞƌ͕
YKVJ VJG PWODGT QH GNGEVTQPKE UJGNNU CTQWPF KVU PWENGWU ƚŚĞ ǀĂŶ ĚĞƌ tĂĂůƐ͛ ƌĂĚŝŝ ĂƌĞ ƚĂŬĞŶ ĂƐ
Ă ŵĞĂƐƵƌĞ ŽĨ ƚŚĞŝƌ ĂƚŽŵŝĐ ƌĂĚŝŝ͘
Explanation: The distance between the outermost shell and the nucleus ͻ
KPETGCUGU YKVJ VJG PWODGT QH GNGEVTQPKE UJGNNU QH CP CVQO dŚĞ ĂƚŽŵŝĐ ƌĂĚŝƵƐ ŽĨ ŵĞƚĂůƐ ŝƐ ĂůƐŽ
Nuclear charge. The size of the atom of an element decreases with an ĐĂůůĞĚ ŵĞƚĂůůŝĐ ƌĂĚŝƵƐ͘
KPETGCUG KP VJG PWENGCT EJCTIG QT CVQOKE PWODGT QH CP CVQO ͻ
ƚŽŵŝĐ ƐŝnjĞ ŽĨ ĂŶ ĞůĞŵĞŶƚ ŝƐ
Explanation: The increased nuclear charge exerts greater force of ĚĞƐĐƌŝďĞĚ ďLJ ŝƚƐ ĂƚŽŵŝĐ ƌĂĚŝƵƐ͘
CVVTCEVKQP QP VJG GNGEVTQPU 6JKU ECWUGU UJTKPMCIG QH VJG GNGEVTQPKE UJGNNU ƚŽŵŝĐ ƌĂĚŝŝ ĂƌĞ ĐŽŵŵŽŶůLJ
VJGTGD[ FGETGCUKPI VJG CVQOKE UK\G ĞdžƉƌĞƐƐĞĚ ŝŶ ŶŐƐƚƌŽŵ ; Ϳ͕
ŶĂŶŽŵĞƚƌĞ ;ŶŵͿ Žƌ ƉŝĐŽŵĞƚƌĞ ;ƉŵͿ
ƵŶŝƚƐ͘
How does atomic size vary in a group of the periodic table ϭ с ϭϬ ʹϭϬ ŵ с ϭϬ Đŵ
–8
–7
–9
In any group of elements, the atomic size increases while going from top ϭ Ŷŵ с ϭϬ ŵ с ϭϬ Đŵ
ʹϭϮ
ʹϭϬ
to the bottom in any group 6JKU ECP DG GZRNCKPGF CU HQNNQYU ϭ Ɖŵ с ϭϬ ŵ с ϭϬ Đŵ
Explanation: When we go down the group, at each new element, a
PGY UJGNN QH GNGEVTQPU KU CFFGF VQ VJG CVQO 6JKU KPETGCUGU VJG UK\G QH VJG
CVQO CV GCEJ PGY GNGOGPV FQYP VJG ITQWR (QT GZCORNG VJG CVQOKE UK\G QH
group 1 and group 17 elements follows the order :
Li < Na < K < Rb < Cs and F < Cl < Br < I
Thus, atom of the last element in any group is the largest atom in that
group
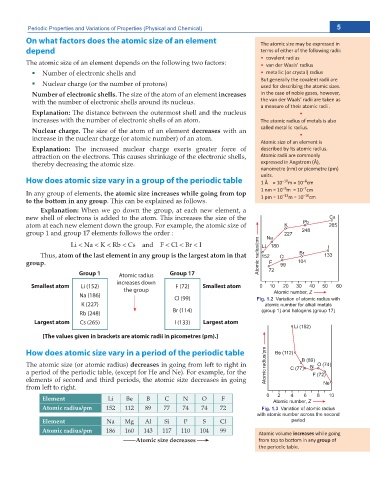
Group 1 Atomic radius Group 17
increases down
Smallest atom Li (152) F (72) Smallest atom
the group
Na (186)
Cl (99) Fig. 1.2 Variation of atomic radius with
K (227) atomic number for alkali metals
Br (114) (group 1) and halogens (group 17)
Rb (248)
Largest atom Cs (265) I (133) Largest atom
[The values given in brackets are atomic radii in picometres (pm).]
How does atomic size vary in a period of the periodic table
The atomic size (or atomic radius) decreases in going from left to right in
C RGTKQF QH VJG RGTKQFKE VCDNG GZEGRV HQT *G CPF 0G (QT GZCORNG HQT VJG
elements of second and third periods, the atomic size decreases in going
HTQO NGHV VQ TKIJV
Element Li Be B C N O F
Atomic radius/pm 152 112 89 77 74 74 72 Fig. 1.3 Variation of atomic radius
with atomic number across the second
Element Na Mg Al Si P S Cl period
Atomic radius/pm 186 160 143 117 110 104 99
ƚŽŵŝĐ ǀŽůƵŵĞ ŝŶĐƌĞĂƐĞƐ ǁŚŝůĞ ŐŽŝŶŐ
Atomic size decreases ĨƌŽŵ ƚŽƉ ƚŽ ďŽƩŽŵ ŝŶ ĂŶLJ ŐƌŽƵƉ ŽĨ
ƚŚĞ ƉĞƌŝŽĚŝĐ ƚĂďůĞ͘