Page 27 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 27
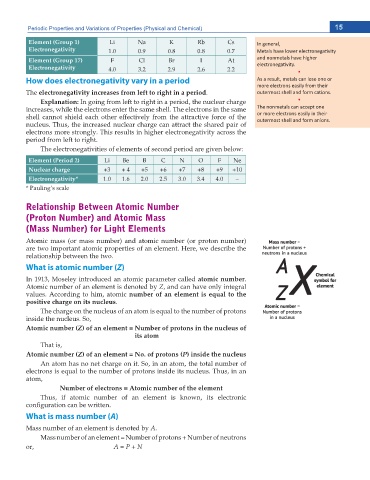
Periodic Properties and Variations of Properties (Physical and Chemical) 15
Element (Group 1) Li Na K Rb Cs /Ŷ ŐĞŶĞƌĂů͕
Electronegativity DĞƚĂůƐ ŚĂǀĞ ůŽǁĞƌ ĞůĞĐƚƌŽŶĞŐĂƟǀŝƚLJ
Element (Group 17) F Cl Br I At ĂŶĚ ŶŽŶŵĞƚĂůƐ ŚĂǀĞ ŚŝŐŚĞƌ
Electronegativity ĞůĞĐƚƌŽŶĞŐĂƟǀŝƚLJ͘ ͻ
How does electronegativity vary in a period Ɛ Ă ƌĞƐƵůƚ͕ ŵĞƚĂůƐ ĐĂŶ ůŽƐĞ ŽŶĞ Žƌ
ŵŽƌĞ ĞůĞĐƚƌŽŶƐ ĞĂƐŝůLJ ĨƌŽŵ ƚŚĞŝƌ
The electronegativity increases from left to right in a period ŽƵƚĞƌŵŽƐƚ ƐŚĞůů ĂŶĚ ĨŽƌŵ ĐĂƟŽŶƐ͘
Explanation: In going from left to right in a period, the nuclear charge ͻ
KPETGCUGU YJKNG VJG GNGEVTQPU GPVGT VJG UCOG UJGNN 6JG GNGEVTQPU KP VJG UCOG dŚĞ ŶŽŶŵĞƚĂůƐ ĐĂŶ ĂĐĐĞƉƚ ŽŶĞ
shell cannot shield each other effectively from the attractive force of the Žƌ ŵŽƌĞ ĞůĞĐƚƌŽŶƐ ĞĂƐŝůLJ ŝŶ ƚŚĞŝƌ
ŽƵƚĞƌŵŽƐƚ ƐŚĞůů ĂŶĚ ĨŽƌŵ ĂŶŝŽŶƐ͘
PWENGWU 6JWU VJG KPETGCUGF PWENGCT EJCTIG ECP CVVTCEV VJG UJCTGF RCKT QH
GNGEVTQPU OQTG UVTQPIN[ 6JKU TGUWNVU KP JKIJGT GNGEVTQPGICVKXKV[ CETQUU VJG
RGTKQF HTQO NGHV VQ TKIJV
The electronegativities of elements of second period are given below:
Element (Period 2) Li Be B C N O F Ne
Nuclear charge +3 + 4 +5 +6 +7 +8 +9 +10
Electronegativity* –
2CWNKPIŏU UECNG
Relationship Between Atomic Number
(Proton Number) and Atomic Mass
(Mass Number) for Light Elements
Atomic mass (or mass number) and atomic number (or proton number)
CTG VYQ KORQTVCPV CVQOKE RTQRGTVKGU QH CP GNGOGPV *GTG YG FGUETKDG VJG
TGNCVKQPUJKR DGVYGGP VJG VYQ
What is atomic number (Z)
In 1913, Moseley introduced an atomic parameter called atomic number
Atomic number of an element is denoted by Z, and can have only integral
XCNWGU #EEQTFKPI VQ JKO CVQOKE number of an element is equal to the
positive charge on its nucleus
The charge on the nucleus of an atom is equal to the number of protons
KPUKFG VJG PWENGWU 5Q
Atomic number (Z) of an element = Number of protons in the nucleus of
its atom
That is,
Atomic number (Z) of an element = No. of protons (P) inside the nucleus
#P CVQO JCU PQ PGV EJCTIG QP KV 5Q KP CP CVQO VJG VQVCN PWODGT QH
GNGEVTQPU KU GSWCN VQ VJG PWODGT QH RTQVQPU KPUKFG KVU PWENGWU 6JWU KP CP
atom,
Number of electrons = Atomic number of the element
Thus, if atomic number of an element is known, its electronic
EQPſIWTCVKQP ECP DG YTKVVGP
What is mass number (A)
Mass number of an element is denoted by A
Mass number of an element = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
or, A = P + N