Page 28 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 28
16 ICSE Chemistry – 10
Then N = A – P
0Q QH PGWVTQPU KP CP CVQO /CUU PQ Ō 0Q QH RTQVQPU KP VJCV CVQO
The number of protons (P) inside the nucleus of an atom is equal to
the atomic number (Z QH VJCV GNGOGPV
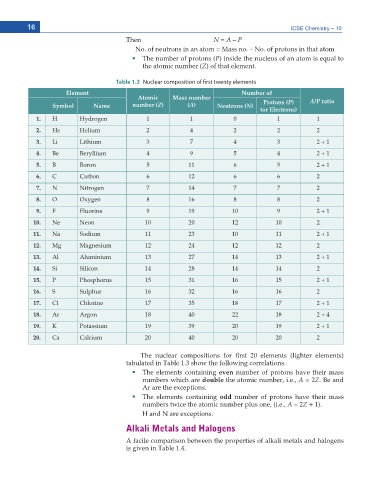
Table 1.3 Nuclear composition of first twenty elements
Element Number of
Atomic Mass number A/P ratio
Symbol Name number (Z) (A) Neutrons (N) Protons (P)
(or Electrons)
1. H Hydrogen 1 1 0 1 1
2. He Helium 2 4 2 2 2
3. Li Lithium 3 7 4 3 2 + 1
4. Be Beryllium 4 9 5 4 2 + 1
5. B Boron 5 11 6 5 2 + 1
6. C Carbon 6 12 6 6 2
7. N Nitrogen 7 14 7 7 2
8. O Oxygen 8 16 8 8 2
9. F Fluorine 9 19 10 9 2 + 1
10. Ne Neon 10 20 12 10 2
11. Na Sodium 11 23 10 11 2 + 1
12. Mg Magnesium 12 24 12 12 2
13. Al Aluminium 13 27 14 13 2 + 1
14. Si Silicon 14 28 14 14 2
15. P Phosphorus 15 31 16 15 2 + 1
16. S Sulphur 16 32 16 16 2
17. Cl Chlorine 17 35 18 17 2 + 1
18. Ar Argon 18 40 22 18 2 + 4
19. K Potassium 19 39 20 19 2 + 1
20. Ca Calcium 20 40 20 20 2
6JG PWENGCT EQORQUKVKQPU HQT ſTUV GNGOGPVU NKIJVGT GNGOGPVU
VCDWNCVGF KP 6CDNG UJQY VJG HQNNQYKPI EQTTGNCVKQPU
The elements containing even number of protons have their mass
numbers which are double VJG CVQOKE PWODGT K G A = 2Z $G CPF
#T CTG VJG GZEGRVKQPU
The elements containing odd number of protons have their mass
PWODGTU VYKEG VJG CVQOKE PWODGT RNWU QPG K G A = 2Z
* CPF 0 CTG GZEGRVKQPU
Alkali Metals and Halogens
A facile comparison between the properties of alkali metals and halogens
KU IKXGP KP 6CDNG