Page 255 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 255
Study of Compounds–Nitric Acid 241
Oxidation Reactions of Nitric Acid with Some
Compounds
Hydrogen sulphide to sulphur
H S + 2HNO o 2H O + 2NO + Sp
2
2
2
3
(conc.)
3H S + 2HNO o 4H O + 2NO + 3S
2
3
2
2
(dilute)
Sulphur dioxide to sulphuric acid
SO 2 + 2HNO o H SO + 2NO n
4
2
2
3
(conc.)
2HNO + 3SO + 2H O o 3H SO + 2NO
2
2
3
2
4
(dilute)
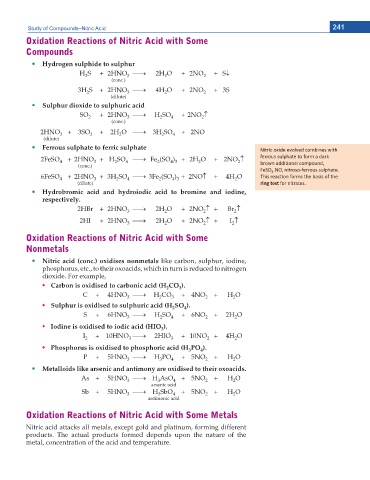
Ferrous sulphate to ferric sulphate EŝƚƌŝĐ ŽdžŝĚĞ ĞǀŽůǀĞĚ ĐŽŵďŝŶĞƐ ǁŝƚŚ
2FeSO + 2HNO + H SO o Fe (SO ) + 2H O + 2NO n ĨĞƌƌŽƵƐ ƐƵůƉŚĂƚĞ ƚŽ ĨŽƌŵ Ă ĚĂƌŬ
4 3
3
2
4
2
2
4
2
(conc.) ďƌŽǁŶ ĂĚĚŝƟŽŶĂů ĐŽŵƉŽƵŶĚ͕
FeSO ͘EK͕ ŶŝƚƌŽƐŽͲĨĞƌƌŽƵƐ ƐƵůƉŚĂƚĞ͘
ϰ
6FeSO + 2HNO + 3H SO o 3Fe (SO ) + 2NOn + 4H O dŚŝƐ ƌĞĂĐƟŽŶ ĨŽƌŵƐ ƚŚĞ ďĂƐŝƐ ŽĨ ƚŚĞ
3
4
2
2
4 3
2
4
(dilute) ring test ĨŽƌ ŶŝƚƌĂƚĞƐ͘
Hydrobromic acid and hydroiodic acid to bromine and iodine,
respectively.
2HBr + 2HNO o 2H O + 2NO n + Br n
3
2
2
2
2HI + 2HNO o 2H O + 2NO n + I n
2
2
2
3
Oxidation Reactions of Nitric Acid with Some
Nonmetals
Nitric acid (conc.) oxidises nonmetals like carbon, sulphur, iodine,
phosphorus, etc., to their oxoacids, which in turn is reduced to nitrogen
dioxide. For example,
Carbon is oxidised to carbonic acid (H CO ).
2
3
C + 4HNO o H CO + 4NO + H O
2
2
3
2
3
Sulphur is oxidised to sulphuric acid (H SO ).
4
2
S + 6HNO o H SO + 6NO + 2H O
2
4
2
3
2
Iodine is oxidised to iodic acid (HIO ).
3
I + 10HNO o 2HIO + 10NO + 4H O
3
2
2
2
3
Phosphorus is oxidised to phosphoric acid (H PO ).
4
3
P + 5HNO o H PO + 5NO + H O
2
3
3
4
2
Metalloids like arsenic and antimony are oxidised to their oxoacids.
As + 5HNO o H AsO + 5NO + H O
2
2
3
3
4
arsenic acid
Sb + 5HNO o H SbO + 5NO + H O
2
4
2
3
3
antimonic acid
Oxidation Reactions of Nitric Acid with Some Metals
Nitric acid attacks all metals, except gold and platinum, forming different
products. The actual products formed depends upon the nature of the
metal, concentration of the acid and temperature.