Page 34 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 34
22 ICSE Chemistry – 10
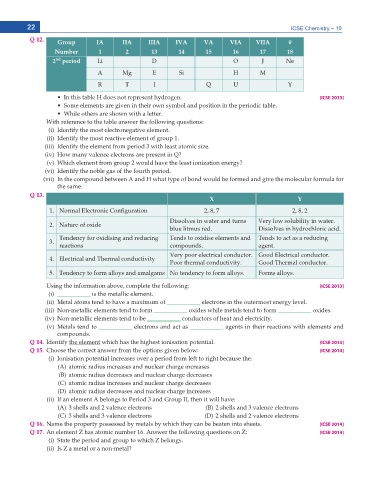
Q 12. Group IA IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 0
Number 1 2 13 14 15 16 17 18
nd
2 period Li D O , Ne
A Mg E Si H M
R T I Q U Y
Ŗ +P VJKU VCDNG * FQGU PQV TGRTGUGPV J[FTQIGP [ICSE 2013]
Ŗ 5QOG GNGOGPVU CTG IKXGP KP VJGKT QYP U[ODQN CPF RQUKVKQP KP VJG RGTKQFKE VCDNG
Ŗ 9JKNG QVJGTU CTG UJQYP YKVJ C NGVVGT
With reference to the table answer the following questions:
K +FGPVKH[ VJG OQUV GNGEVTQPGICVKXG GNGOGPV
KK +FGPVKH[ VJG OQUV TGCEVKXG GNGOGPV QH ITQWR
KKK +FGPVKH[ VJG GNGOGPV HTQO RGTKQF YKVJ NGCUV CVQOKE UK\G
(iv) How many valence electrons are present in Q?
(v) Which element from group 2 would have the least ionization energy?
XK +FGPVKH[ VJG PQDNG ICU QH VJG HQWTVJ RGTKQF
(vii) In the compound between A and H what type of bond would be formed and give the molecular formula for
VJG UCOG
Q 13.
X Y
0QTOCN 'NGEVTQPKE %QPſIWTCVKQP 2, 8, 7 2, 8, 2
Dissolves in water and turns 8GT[ NQY UQNWDKNKV[ KP YCVGT
Nature of oxide
DNWG NKVOWU TGF &KUUQNXGU KP J[FTQEJNQTKE CEKF
Tendency for oxidising and reducing Tends to oxidise elements and Tends to act as a reducing
reactions EQORQWPFU CIGPV
8GT[ RQQT GNGEVTKECN EQPFWEVQT )QQF 'NGEVTKECN EQPFWEVQT
Electrical and Thermal conductivity
2QQT VJGTOCN EQPFWEVKXKV[ )QQF 6JGTOCN EQPFWEVQT
Tendency to form alloys and amalgams 0Q VGPFGPE[ VQ HQTO CNNQ[U (QTOU CNNQ[U
Using the information above, complete the following: [ICSE 2013]
(i) ___________ KU VJG OGVCNNKE GNGOGPV
(ii) Metal atoms tend to have a maximum of ___________ GNGEVTQPU KP VJG QWVGTOQUV GPGTI[ NGXGN
(iii) Non-metallic elements tend to form ___________ oxides while metals tend to form ___________ QZKFGU
(iv) Non-metallic elements tend to be ___________ EQPFWEVQTU QH JGCV CPF GNGEVTKEKV[
(v) Metals tend to ___________ electrons and act as ___________ agents in their reactions with elements and
EQORQWPFU
Q 14. Identify the element YJKEJ JCU VJG JKIJGUV KQPKUCVKQP RQVGPVKCN [ICSE 2013]
Q 15. Choose the correct answer from the options given below: [ICSE 2014]
(i) Ionisation potential increases over a period from left to right because the:
(A) atomic radius increases and nuclear charge increases
(B) atomic radius decreases and nuclear charge decreases
(C) atomic radius increases and nuclear charge decreases
(D) atomic radius decreases and nuclear charge increases
KK +H CP GNGOGPV # DGNQPIU VQ 2GTKQF CPF )TQWR ++ VJGP KV YKNN JCXG
(A) 3 shells and 2 valence electrons (B) 2 shells and 3 valence electrons
(C) 3 shells and 3 valence electrons (D) 2 shells and 2 valence electrons
Q 16. 0COG VJG RTQRGTV[ RQUUGUUGF D[ OGVCNU D[ YJKEJ VJG[ ECP DG DGCVGP KPVQ UJGGVU [ICSE 2014]
Q 17. #P GNGOGPV < JCU CVQOKE PWODGT #PUYGT VJG HQNNQYKPI SWGUVKQPU QP < [ICSE 2014]
K 5VCVG VJG RGTKQF CPF ITQWR VQ YJKEJ < DGNQPIU
(ii) Is Z a metal or a non-metal?