Page 19 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 19
The Language of Chemistry 7
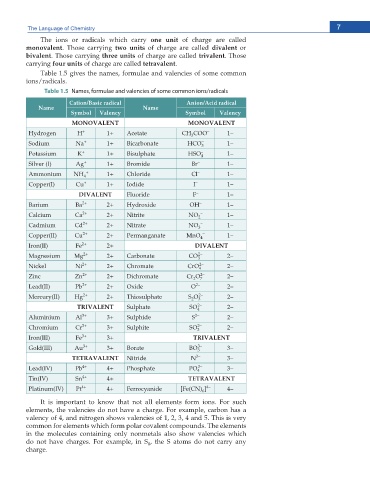
The ions or radicals which carry one unit of charge are called
monovalent. Those carrying two units of charge are called divalent or
bivalent. Those carrying three units of charge are called trivalent. Those
carrying four units of charge are called tetravalent.
Table 1.5 gives the names, formulae and valencies of some common
ions/radicals.
Table 1.5 Names, formulae and valencies of some common ions/radicals
Cation/Basic radical Anion/Acid radical
Name Name
Symbol Valency Symbol Valency
MONOVALENT MONOVALENT
Hydrogen H + 1+ Acetate CH COO – 1–
3
Sodium Na + 1+ Bicarbonate HCO 3 – 1–
Potassium K + 1+ Bisulphate HSO – 4 1–
Silver (I) Ag + 1+ Bromide Br – 1–
Ammonium NH 4 + 1+ Chloride Cl – 1–
Copper(I) Cu + 1+ Iodide I – 1–
DIVALENT Fluoride F – 1–
Barium Ba 2+ 2+ Hydroxide OH – 1–
Calcium Ca 2+ 2+ Nitrite NO 2 – 1–
Cadmium Cd 2+ 2+ Nitrate NO 3 – 1–
Copper(II) Cu 2+ 2+ Permanganate MnO 4 – 1–
Iron(II) Fe 2+ 2+ DIVALENT
Magnesium Mg 2+ 2+ Carbonate CO 3 2– 2–
Nickel Ni 2+ 2+ Chromate CrO 4 2– 2–
Zinc Zn 2+ 2+ Dichromate Cr O 2– 2–
7
2
Lead(II) Pb 2+ 2+ Oxide O 2– 2–
Mercury(II) Hg 2+ 2+ Thiosulphate S O 3 2– 2–
2
TRIVALENT Sulphate SO 4 2– 2–
Aluminium Al 3+ 3+ Sulphide S 2– 2–
Chromium Cr 3+ 3+ Sulphite SO 3 2– 2–
Iron(III) Fe 3+ 3+ TRIVALENT
Gold(III) Au 3+ 3+ Borate BO 3– 3–
3
TETRAVALENT Nitride N 3– 3–
Lead(IV) Pb 4+ 4+ Phosphate PO 4 3– 3–
Tin(IV) Sn 4+ 4+ TETRAVALENT
Platinum(IV) Pt 4+ 4+ Ferrocyanide [Fe(CN) ] 4– 4–
6
It is important to know that not all elements form ions. For such
elements, the valencies do not have a charge. For example, carbon has a
valency of 4, and nitrogen shows valencies of 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. This is very
common for elements which form polar covalent compounds. The elements
in the molecules containing only nonmetals also show valencies which
do not have charges. For example, in S , the S atoms do not carry any
8
charge.