Page 21 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 21
The Language of Chemistry 9
and nitrogen (N ) are termed as diatomic molecules, K G , their
2
atomicity is two.
Both, the molecules of water (H O) and carbon dioxide (CO ) contain
2
2
three atoms each. Therefore, these are termed as triatomic molecules.
The number of atoms of all the elements in a molecule of any
substance (element or compound) is called its atomicity.
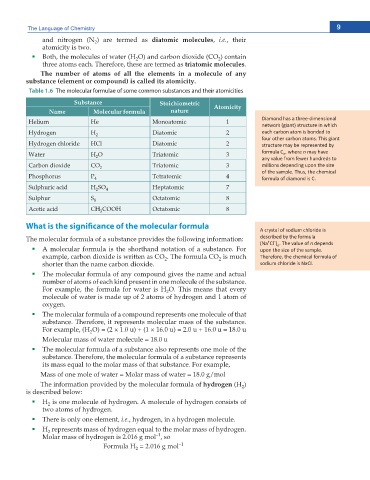
Table 1.6 The molecular formulae of some common substances and their atomicities
Substance Stoichiometric
Name Molecular formula nature Atomicity
Helium He Monoatomic 1 ŝĂŵŽŶĚ ŚĂƐ Ă ƚŚƌĞĞͲĚŝŵĞŶƐŝŽŶĂů
ŶĞƚǁŽƌŬ ;ŐŝĂŶƚͿ ƐƚƌƵĐƚƵƌĞ ŝŶ ǁŚŝĐŚ
Hydrogen H 2 Diatomic 2 ĞĂĐŚ ĐĂƌďŽŶ ĂƚŽŵ ŝƐ ďŽŶĚĞĚ ƚŽ
ĨŽƵƌ ŽƚŚĞƌ ĐĂƌďŽŶ ĂƚŽŵƐ͘ dŚŝƐ ŐŝĂŶƚ
Hydrogen chloride HCl Diatomic 2 ƐƚƌƵĐƚƵƌĞ ŵĂLJ ďĞ ƌĞƉƌĞƐĞŶƚĞĚ ďLJ
Water H O Triatomic 3 ĨŽƌŵƵůĂ ͕ ǁŚĞƌĞ n ŵĂLJ ŚĂǀĞ
n
2
ĂŶLJ ǀĂůƵĞ ĨƌŽŵ ĨĞǁĞƌ ŚƵŶĚƌĞĚƐ ƚŽ
Carbon dioxide CO 2 Triatomic 3 ŵŝůůŝŽŶƐ ĚĞƉĞŶĚŝŶŐ ƵƉŽŶ ƚŚĞ ƐŝnjĞ
ŽĨ ƚŚĞ ƐĂŵƉůĞ͘ dŚƵƐ͕ ƚŚĞ ĐŚĞŵŝĐĂů
Phosphorus P 4 Tetratomic 4 ĨŽƌŵƵůĂ ŽĨ ĚŝĂŵŽŶĚ ŝƐ ͘
Sulphuric acid H SO 4 Heptatomic 7
2
Sulphur S 8 Octatomic 8
Acetic acid CH COOH Octatomic 8
3
What is the significance of the molecular formula
ĐƌLJƐƚĂů ŽĨ ƐŽĚŝƵŵ ĐŚůŽƌŝĚĞ ŝƐ
The molecular formula of a substance provides the following information: ĚĞƐĐƌŝďĞĚ ďLJ ƚŚĞ ĨŽƌŵƵůĂ
–
+
;EĂ ů ) ͘ dŚĞ ǀĂůƵĞ ŽĨ n ĚĞƉĞŶĚƐ
n
A molecular formula is the shorthand notation of a substance. For ƵƉŽŶ ƚŚĞ ƐŝnjĞ ŽĨ ƚŚĞ ƐĂŵƉůĞ͘
example, carbon dioxide is written as CO . The formula CO is much dŚĞƌĞĨŽƌĞ͕ ƚŚĞ ĐŚĞŵŝĐĂů ĨŽƌŵƵůĂ ŽĨ
2
2
shorter than the name carbon dioxide. ƐŽĚŝƵŵ ĐŚůŽƌŝĚĞ ŝƐ EĂ /͘
The molecular formula of any compound gives the name and actual
number of atoms of each kind present in one molecule of the substance.
For example, the formula for water is H O. This means that every
2
molecule of water is made up of 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of
oxygen.
The molecular formula of a compound represents one molecule of that
substance. Therefore, it represents molecular mass of the substance.
For example, (H O) = (2 × 1.0 u) + (1 × 16.0 u) = 2.0 u + 16.0 u = 18.0 u
2
Molecular mass of water molecule = 18.0 u
The molecular formula of a substance also represents one mole of the
substance. Therefore, the molecular formula of a substance represents
its mass equal to the molar mass of that substance. For example,
Mass of one mole of water = Molar mass of water = 18.0 g/mol
The information provided by the molecular formula of hydrogen (H )
2
is described below:
H is one molecule of hydrogen. A molecule of hydrogen consists of
2
two atoms of hydrogen.
There is only one element, K G , hydrogen, in a hydrogen molecule.
H represents mass of hydrogen equal to the molar mass of hydrogen.
2
–1
Molar mass of hydrogen is 2.016 g mol , so
Formula H = 2.016 g mol –1
2