Page 63 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 63
Chemical Changes and Reactions 51
Addition of oxygen into the atmosphere: Oxygen is produced when
Green plants make food from carbon dioxide and water in the
presence of sunlight. This process is called photosynthesis. The
released oxygen escapes into the air.
Ozone decomposes to produce oxygen.
2O (g) o 3O (g)
3
2
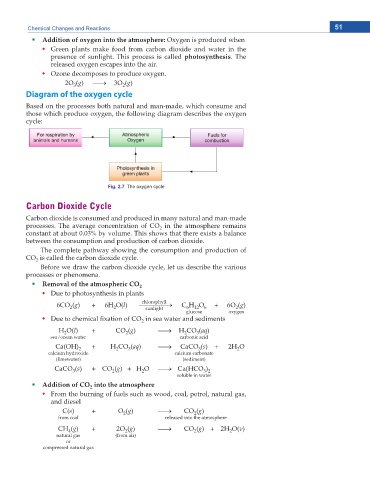
Diagram of the oxygen cycle
Based on the processes both natural and man-made, which consume and
those which produce oxygen, the following diagram describes the oxygen
cycle:
Fig. 2.7 The oxygen cycle
Carbon Dioxide Cycle
Carbon dioxide is consumed and produced in many natural and man-made
processes. The average concentration of CO in the atmosphere remains
2
constant at about 0.03% by volume. This shows that there exists a balance
between the consumption and production of carbon dioxide.
The complete pathway showing the consumption and production of
CO is called the carbon dioxide cycle.
2
Before we draw the carbon dioxide cycle, let us describe the various
processes or phenomena.
Removal of the atmospheric CO
2
Due to photosynthesis in plants
chlorophyll
6CO (g) + 6H O(l) o C H O + 6O (g)
12
6
2
2
2
6
sunlight
glucose oxygen
Due to chemical xation of CO in sea water and sediments
2
H O(l) + CO (g) o H CO (aq)
2
3
2
2
sea/ocean water carbonic acid
Ca(OH) 2 + H CO (aq) o CaCO (s) + 2H O
2
3
3
2
calcium hydroxide calcium carbonate
(limewater) (sediment)
CaCO (s) + CO (g) + H O o Ca(HCO )
3 2
2
3
2
soluble in water
Addition of CO into the atmosphere
2
From the burning of fuels such as wood, coal, petrol, natural gas,
and diesel
C(s) + O (g) o CO (g)
2
2
from coal released into the atmosphere
CH (g) + 2O (g) o CO (g) + 2H O(v)
4
2
2
2
natural gas (from air)
or
compressed natural gas