Page 58 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 58
46 ICSE Chemistry – 9
What is meant by a supporter of combustion
A substance which helps in combustion (or burning) of any combustible
material is called a supporter of combustion (or oxidiser). For example,
during the combustion of carbon, oxygen (or air) is a supporter of
combustion.
Nitrous oxide (N O) is another supporter of combustion. Nitrous
2
oxide supports combustion more vigorously than air. This is because on
decomposition, nitrous oxide gives a gas mixture containing one-third of
its volume as oxygen, whereas air contains only QPG ſHVJ of its volume as
oxygen.
600°C
2N O(g) o 2N (g) + O (g)
2
2
2
nitrous oxide nitrogen oxygen
(2 : 1 by volume)
What are the necessary conditions for the combustion or
burning to take place
The following conditions are necessary for the combustion or burning to
take place:
The presence of a combustible substance. A substance which burns
readily is called a combustible substance. So, for combustion to take
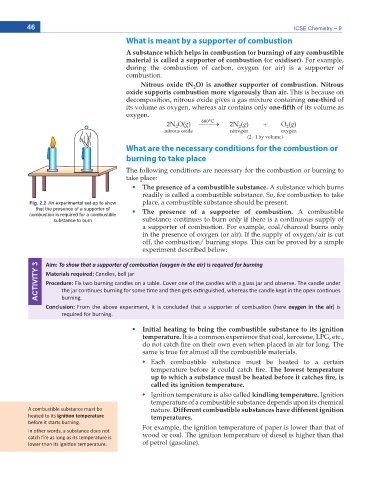
Fig. 2.2 An experimental set-up to show place, a combustible substance should be present.
that the presence of a supporter of The presence of a supporter of combustion. A combustible
combustion is required for a combustible
substance to burn substance continues to burn only if there is a continuous supply of
a supporter of combustion. For example, coal/charcoal burns only
in the presence of oxygen (or air). If the supply of oxygen/air is cut
off, the combustion/ burning stops. This can be proved by a simple
experiment described below:
ACTIVITY 3 Materials required: ĂŶĚůĞƐ͕ ďĞůů ũĂƌ
Aim: dŽ ƐŚŽǁ ƚŚĂƚ Ă ƐƵƉƉŽƌƚĞƌ ŽĨ ĐŽŵďƵƐƟŽŶ ;ŽdžLJŐĞŶ ŝŶ ƚŚĞ ĂŝƌͿ ŝƐ ƌĞƋƵŝƌĞĚ ĨŽƌ ďƵƌŶŝŶŐ
Procedure: &ŝdž ƚǁŽ ďƵƌŶŝŶŐ ĐĂŶĚůĞƐ ŽŶ Ă ƚĂďůĞ͘ ŽǀĞƌ ŽŶĞ ŽĨ ƚŚĞ ĐĂŶĚůĞƐ ǁŝƚŚ Ă ŐůĂƐƐ ũĂƌ ĂŶĚ ŽďƐĞƌǀĞ͘ dŚĞ ĐĂŶĚůĞ ƵŶĚĞƌ
ƚŚĞ ũĂƌ ĐŽŶƟŶƵĞƐ ďƵƌŶŝŶŐ ĨŽƌ ƐŽŵĞ ƟŵĞ ĂŶĚ ƚŚĞŶ ŐĞƚƐ ĞdžƟŶŐƵŝƐŚĞĚ͕ ǁŚĞƌĞĂƐ ƚŚĞ ĐĂŶĚůĞ ŬĞƉƚ ŝŶ ƚŚĞ ŽƉĞŶ ĐŽŶƟŶƵĞƐ
ďƵƌŶŝŶŐ͘
Conclusion: &ƌŽŵ ƚŚĞ ĂďŽǀĞ ĞdžƉĞƌŝŵĞŶƚ͕ ŝƚ ŝƐ ĐŽŶĐůƵĚĞĚ ƚŚĂƚ Ă ƐƵƉƉŽƌƚĞƌ ŽĨ ĐŽŵďƵƐƟŽŶ ;ŚĞƌĞ oxygen in the airͿ ŝƐ
ƌĞƋƵŝƌĞĚ ĨŽƌ ďƵƌŶŝŶŐ͘
Initial heating to bring the combustible substance to its ignition
temperature. It is a common experience that coal, kerosene, LPG, etc.,
do not catch re on their own even when placed in air for long. The
same is true for almost all the combustible materials.
Each combustible substance must be heated to a certain
temperature before it could catch re. The lowest temperature
WR VQ YJKEJ C UWDUVCPEG OWUV DG JGCVGF DGHQTG KV ECVEJGU ſTG KU
called its ignition temperature.
Ignition temperature is also called kindling temperature. Ignition
temperature of a combustible substance depends upon its chemical
ĐŽŵďƵƐƟďůĞ ƐƵďƐƚĂŶĐĞ ŵƵƐƚ ďĞ nature. Different combustible substances have different ignition
ŚĞĂƚĞĚ ƚŽ ŝƚƐ igniƟon temperature temperatures.
ďĞĨŽƌĞ ŝƚ ƐƚĂƌƚƐ ďƵƌŶŝŶŐ͘
For example, the ignition temperature of paper is lower than that of
/Ŷ ŽƚŚĞƌ ǁŽƌĚƐ͕ Ă ƐƵďƐƚĂŶĐĞ ĚŽĞƐ ŶŽƚ wood or coal. The ignition temperature of diesel is higher than that
ĐĂƚĐŚ ĮƌĞ ĂƐ ůŽŶŐ ĂƐ ŝƚƐ ƚĞŵƉĞƌĂƚƵƌĞ ŝƐ
ůŽǁĞƌ ƚŚĂŶ ŝƚƐ ŝŐŶŝƟŽŶ ƚĞŵƉĞƌĂƚƵƌĞ͘ of petrol (gasoline).