Page 170 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 170
156 ICSE Chemistry – 10
How does concentration of an ion in solution affect its
discharge at the respective electrode
The higher the concentration of an ion in the solution, higher is its tendency
for discharge at the respective electrode in preference to the ion having
lower concentration. For example,
Electrolyte Ions present in Ions migrating to Ion discharged at Product formed at
the solution anode cathode anode cathode anode cathode
–
+
–
Dil. HCl(aq) H , Cl , OH – Cl , OH – H + OH – H + O 2 H 2
–
+
–
Conc. HCl(aq) H , Cl , OH – Cl , OH – H + Cl – H + Cl 2 H 2
–
–
Here, OH and Cl migrate towards anode. According to the position
–
in the electrochemical series, the OH ion should get discharged in
–
preference to Cl . It is found to be so in dilute solution of hydrochloric acid
[HCl(aq)].
During the electrolysis of concentrated solution of hydrochloric
–
–
acid, both OH and Cl ions migrate towards anode but the ion which
–
–
get discharged is Cl and not OH . This is because the concentration of
–
–
Cl is much higher than that of OH . Therefore, during the electrolysis of
–
–
concentrated HCl(aq), the Cl ions get discharged in preference to OH
ion due to its much higher concentration.
How does the nature of electrode material affect the
discharge of ions at the electrodes
During electrolysis, the following two types of electrodes may be used:
Inert or nonattackable electrode. Electrodes made from carbon or
platinum are called inert/nonattackable electrodes. The inert (or
nonattackable) electrodes do not take part in the electrode reaction
(or redox reaction) during electrolysis.
Active or attackable electrode. Electrodes made from copper,
silver, nickel, etc. are attackable. The active or attackable electrodes
actually take part in the electrode reaction (or redox reaction) during
electrolysis.
The effect of electrode material on the electrode reaction is illustrated
in the electrolysis of copper sulphate using anodes of platinum (inert
electrode) and copper (attackable electrode) on pages 158-159.
Some Examples of Electrolysis
Some typical examples of electrolysis are described here.
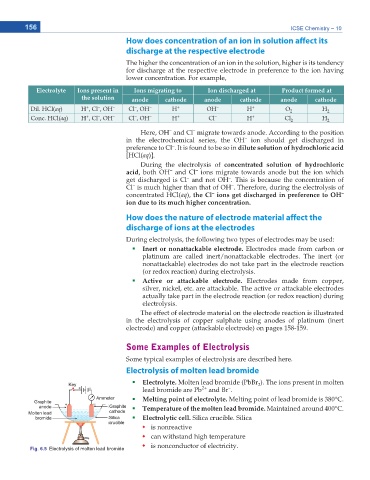
Electrolysis of molten lead bromide
Electrolyte. Molten lead bromide (PbBr ). The ions present in molten
2
2+
–
lead bromide are Pb and Br .
Melting point of electrolyte. Melting point of lead bromide is 380°C.
Temperature of the molten lead bromide. Maintained around 400°C.
Electrolytic cell. Silica crucible. Silica
is nonreactive
can withstand high temperature
is nonconductor of electricity.
Fig. 6.5 Electrolysis of molten lead bromide