Page 171 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 171
Electrolysis 157
Electrodes. Graphite (or carbon) rods (or plates) are used as cathode
and anode. Graphite remains unaffected by the reactive bromine
vapour.
Electrode reactions. Given below.
Products of electrolysis. The products of electrolysis at the two
electrodes are,
at cathode. Lead metal (Greyish in colour)
at anode. Bromine (Reddish-brown vapour)
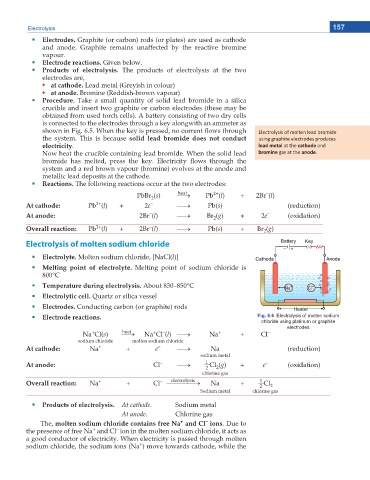
Procedure. Take a small quantity of solid lead bromide in a silica
crucible and insert two graphite or carbon electrodes (these may be
obtained from used torch cells). A battery consisting of two dry cells
is connected to the electrodes through a key alongwith an ammeter as
UJQYP KP (KI 9JGP VJG MG[ KU RTGUUGF PQ EWTTGPV ƀQYU VJTQWIJ ůĞĐƚƌŽůLJƐŝƐ ŽĨ ŵŽůƚĞŶ ůĞĂĚ ďƌŽŵŝĚĞ
the system. This is because solid lead bromide does not conduct ƵƐŝŶŐ ŐƌĂƉŚŝƚĞ ĞůĞĐƚƌŽĚĞƐ ƉƌŽĚƵĐĞƐ
electricity. ůĞĂĚ ŵĞƚĂů Ăƚ ƚŚĞ ĐĂƚŚŽĚĞ ĂŶĚ
Now heat the crucible containing lead bromide. When the solid lead ďƌŽŵŝŶĞ ŐĂƐ Ăƚ ƚŚĞ ĂŶŽĚĞ͘
DTQOKFG JCU OGNVGF RTGUU VJG MG[ 'NGEVTKEKV[ ƀQYU VJTQWIJ VJG
system and a red brown vapour (bromine) evolves at the anode and
metallic lead deposits at the cathode.
Reactions. The following reactions occur at the two electrodes:
heat
2+
–
PbBr (s) o Pb (l) + 2Br (l)
2
2+
–
At cathode: Pb (l) + 2e o Pb(s) (reduction)
–
At anode: 2Br (l) o Br (g) + 2e – (oxidation)
2
2+
–
Overall reaction: Pb (l) + 2Br (l) o Pb(s) + Br (g)
2
Electrolysis of molten sodium chloride
Electrolyte. Molten sodium chloride, [NaCl(l)]
Melting point of electrolyte. Melting point of sodium chloride is
800°C
Temperature during electrolysis. About 830–850°C
Electrolytic cell. Quartz or silica vessel
Electrodes. Conducting carbon (or graphite) rods
Electrode reactions. Fig. 6.6 Electrolysis of molten sodium
chloride using platinum or graphite
electrodes
heat
–
+
+
Na Cl(s) o Na Cl (l) o Na + + Cl –
sodium chloride molten sodium chloride
–
At cathode: Na + + e o Na (reduction)
sodium metal
–
At anode: Cl o 1 Cl (g) + e – (oxidation)
2 2
chlorine gas
electrolysis
–
Overall reaction: Na + + Cl o Na + 1 2 Cl 2
Sodium metal chlorine gas
Products of electrolysis. At cathode. Sodium metal
At anode. Chlorine gas
–
+
The, molten sodium chloride contains free Na and Cl ions. Due to
–
+
the presence of free Na and Cl ion in the molten sodium chloride, it acts as
a good conductor of electricity. When electricity is passed through molten
+
sodium chloride, the sodium ions (Na ) move towards cathode, while the