Page 176 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 176
162 ICSE Chemistry – 10
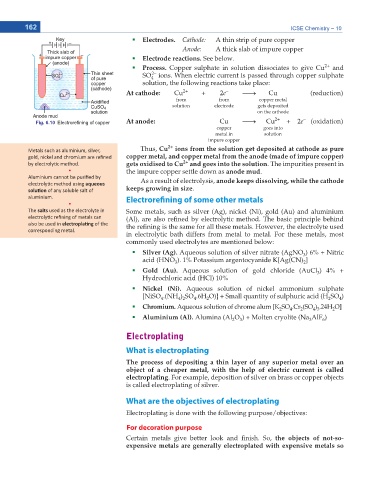
Electrodes. Cathode: A thin strip of pure copper
Anode: A thick slab of impure copper
Electrode reactions. See below.
2+
Process. Copper sulphate in solution dissociates to give Cu and
2–
SO ions. When electric current is passed through copper sulphate
4
solution, the following reactions take place:
–
At cathode: Cu 2+ + 2e o Cu (reduction)
from from copper metal
solution electrode gets deposited
on the cathode
–
2+
Fig. 6.10 (OHFWURUH¿QLQJ RI FRSSHU At anode: Cu o Cu + 2e (oxidation)
copper goes into
metal in solution
impure copper
2+
DĞƚĂůƐ ƐƵĐŚ ĂƐ ĂůƵŵŝŶŝƵŵ͕ ƐŝůǀĞƌ͕ Thus, Cu ions from the solution get deposited at cathode as pure
ŐŽůĚ͕ ŶŝĐŬĞů ĂŶĚ ĐŚƌŽŵŝƵŵ ĂƌĞ ƌĞĮŶĞĚ copper metal, and copper metal from the anode (made of impure copper)
2+
ďLJ ĞůĞĐƚƌŽůLJƟĐ ŵĞƚŚŽĚ͘ gets oxidised to Cu and goes into the solution. The impurities present in
ͻ the impure copper settle down as anode mud.
ůƵŵŝŶŝƵŵ ĐĂŶŶŽƚ ďĞ ƉƵƌŝĮĞĚ ďLJ As a result of electrolysis, anode keeps dissolving, while the cathode
ĞůĞĐƚƌŽůLJƟĐ ŵĞƚŚŽĚ ƵƐŝŶŐ ĂƋƵĞŽƵƐ
ƐŽůƵƟŽŶ ŽĨ ĂŶLJ ƐŽůƵďůĞ ƐĂůƚ ŽĨ keeps growing in size.
ĂůƵŵŝŶŝƵŵ͘ Electrorefining of some other metals
ͻ
dŚĞ ƐĂůƚƐ ƵƐĞĚ ĂƐ ƚŚĞ ĞůĞĐƚƌŽůLJƚĞ ŝŶ Some metals, such as silver (Ag), nickel (Ni), gold (Au) and aluminium
ĞůĞĐƚƌŽůLJƟĐ ƌĞĮŶŝŶŐ ŽĨ ŵĞƚĂůƐ ĐĂŶ #N CTG CNUQ TGſPGF D[ GNGEVTQN[VKE OGVJQF 6JG DCUKE RTKPEKRNG DGJKPF
ĂůƐŽ ďĞ ƵƐĞĚ ŝŶ ĞůĞĐƚƌŽƉůĂƟŶŐ ŽĨ ƚŚĞ VJG TGſPKPI KU VJG UCOG HQT CNN VJGUG OGVCNU *QYGXGT VJG GNGEVTQN[VG WUGF
ĐŽƌƌĞƐƉŽŶĚŝŶŐ ŵĞƚĂů͘
in electrolytic bath differs from metal to metal. For these metals, most
commonly used electrolytes are mentioned below:
Silver (Ag). Aqueous solution of silver nitrate (AgNO ) 6% + Nitric
3
acid (HNO ). 1% Potassium argentocyanide K[Ag(CN) ]
3
2
Gold (Au). Aqueous solution of gold chloride (AuCl ) 4% +
3
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) 10%
Nickel (Ni). Aqueous solution of nickel ammonium sulphate
[NiSO .(NH ) SO .6H O)] + Small quantity of sulphuric acid (H SO )
4 2
4
4
4
2
2
Chromium. Aqueous solution of chrome alum [K SO .Cr (SO ) .24H O]
4
2
2
2
4 3
Aluminium (Al). Alumina (Al O ) + Molten cryolite (Na AlF )
3
6
3
2
Electroplating
What is electroplating
The process of depositing a thin layer of any superior metal over an
object of a cheaper metal, with the help of electric current is called
electroplating. For example, deposition of silver on brass or copper objects
is called electroplating of silver.
What are the objectives of electroplating
Electroplating is done with the following purpose/objectives:
For decoration purpose
%GTVCKP OGVCNU IKXG DGVVGT NQQM CPF ſPKUJ 5Q the objects of not-so-
expensive metals are generally electroplated with expensive metals so