Page 172 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 172
158 ICSE Chemistry – 10
–
chloride ions (Cl ) move towards anode. These ions then undergo the
reactions at the electrode surface as described above.
Electrolysis of water using platinum electrodes
+
Pure water is very feebly ionised. So, the concentration of free H and
–
OH ions in water is very low. As a result, it is a very poor conductor of
electricity. To make it a good conductor of electricity, a small quantity of
sulphuric acid is added to it. Such water is called acidulated water.
Electrolyte. Acidulated water (water containing little sulphuric acid).
HCl(aq) and HNO (aq) cannot be used for acidifying water because
3
they are volatile and give out offensive vapour.
Operating temperature. Room temperature to about 50°C.
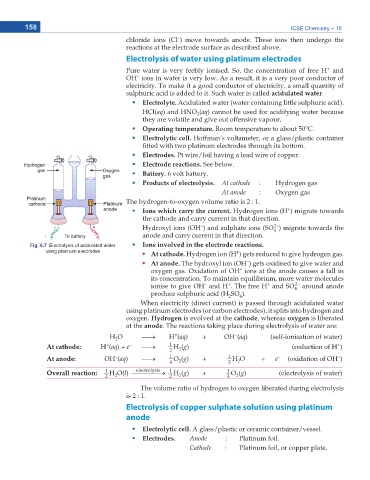
Electrolytic cell. Hoffman’s voltameter, or a glass/plastic container
ſVVGF YKVJ VYQ RNCVKPWO GNGEVTQFGU VJTQWIJ KVU DQVVQO
Electrodes. Pt wire/foil having a lead wire of copper.
Electrode reactions. See below.
Battery. 6 volt battery.
Products of electrolysis. At cathode : Hydrogen gas
At anode : Oxygen gas
The hydrogen-to-oxygen volume ratio is 2 : 1.
+
Ions which carry the current. Hydrogen ions (H ) migrate towards
the cathode and carry current in that direction.
–
2–
Hydroxyl ions (OH ) and sulphate ions (SO ) migrate towards the
4
anode and carry current in that direction.
Fig. 6.7 Electrolysis of acidulated water Ions involved in the electrode reactions.
using platinum electrodes +
At cathode. Hydrogen ion (H ) gets reduced to give hydrogen gas.
–
At anode. The hydroxyl ion (OH ) gets oxidised to give water and
–
oxygen gas. Oxidation of OH ions at the anode causes a fall in
its concentration. To maintain equilibrium, more water molecules
+
+
–
2–
ionise to give OH and H . The free H and SO around anode
4
produce sulphuric acid (H SO ).
2
4
When electricity (direct current) is passed through acidulated water
using platinum electrodes (or carbon electrodes), it splits into hydrogen and
oxygen. Hydrogen is evolved at the cathode, whereas oxygen is liberated
at the anode. The reactions taking place during electrolysis of water are:
+
–
H O o H (aq) + OH (aq) (self-ionisation of water)
2
+
+
–
At cathode: H (aq) + e o 1 2 H (g) (reduction of H )
2
–
–
–
At anode: OH (aq) o 1 4 O (g) + 1 2 H O + e (oxidation of OH )
2
2
1
electrolysis
Overall reaction: 1 2 H O(l) o H (g) + 1 4 O (g) (electrolysis of water)
2
2
2
2
The volume ratio of hydrogen to oxygen liberated during electrolysis
is 2 : 1.
Electrolysis of copper sulphate solution using platinum
anode
Electrolytic cell. A glass/plastic or ceramic container/vessel.
Electrodes. Anode : Platinum foil.
Cathode : Platinum foil, or copper plate.