Page 79 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 79
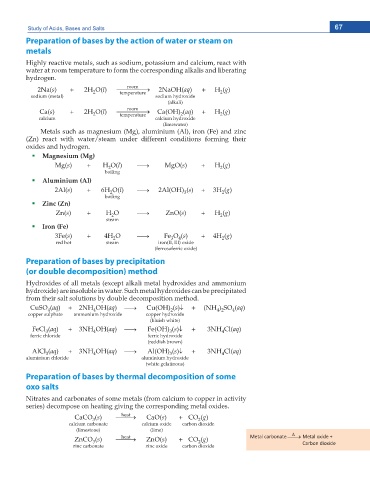
Study of Acids, Bases and Salts 67
Preparation of bases by the action of water or steam on
metals
Highly reactive metals, such as sodium, potassium and calcium, react with
water at room temperature to form the corresponding alkalis and liberating
hydrogen.
room
2Na(s) + 2H O(l) o 2NaOH(aq) + H (g)
2
2
sodium (metal) temperature sodium hydroxide
(alkali)
room
Ca(s) + 2H O(l) o Ca(OH) (aq) + H (g)
2
2
2
temperature
calcium calcium hydroxide
(limewater)
Metals such as magnesium (Mg), aluminium (Al), iron (Fe) and zinc
(Zn) react with water/steam under different conditions forming their
oxides and hydrogen.
Magnesium (Mg)
Mg(s) + H O(l) o MgO(s) + H (g)
2
2
boiling
Aluminium (Al)
2Al(s) + 6H O(l) o 2Al(OH) (s) + 3H (g)
2
2
3
boiling
Zinc (Zn)
Zn(s) + H O o ZnO(s) + H (g)
2
2
steam
Iron (Fe)
3Fe(s) + 4H O o Fe O (s) + 4H (g)
4
2
2
3
red hot steam iron(II, III) oxide
(ferrosoferric oxide)
Preparation of bases by precipitation
(or double decomposition) method
Hydroxides of all metals (except alkali metal hydroxides and ammonium
hydroxide) are insoluble in water. Such metal hydroxides can be precipitated
from their salt solutions by double decomposition method.
CuSO (aq) + 2NH OH(aq) o Cu(OH) (s)p + (NH ) SO (aq)
2
4
4
4
4 2
copper sulphate ammonium hydroxide copper hydroxide
(bluish white)
FeCl (aq) + 3NH OH(aq) o Fe(OH) (s)p + 3NH Cl(aq)
4
4
3
3
ferric chloride ferric hydroxide
(reddish brown)
AlCl (aq) + 3NH OH(aq) o Al(OH) (s)p + 3NH Cl(aq)
3
3
4
4
aluminium chloride aluminium hydroxide
(white gelatinous)
Preparation of bases by thermal decomposition of some
oxo salts
Nitrates and carbonates of some metals (from calcium to copper in activity
series) decompose on heating giving the corresponding metal oxides.
heat
CaCO (s) o CaO(s) + CO (g)
3
2
calcium carbonate calcium oxide carbon dioxide
(limestone) (lime) '
heat
ZnCO (s) o ZnO(s) + CO (g) DĞƚĂů ĐĂƌďŽŶĂƚĞ o DĞƚĂů ŽdžŝĚĞ н
2
3
zinc carbonate zinc oxide carbon dioxide ĂƌďŽŶ ĚŝŽdžŝĚĞ