Page 80 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 80
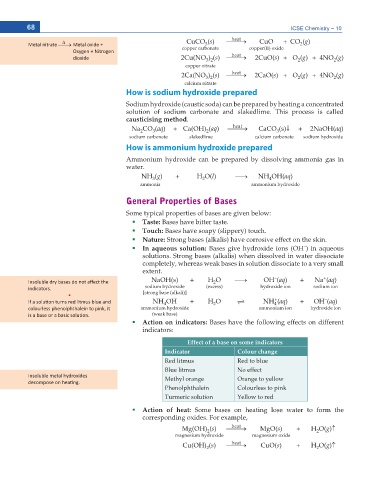
68 ICSE Chemistry – 10
heat
' CuCO (s) o CuO + CO (g)
3
DĞƚĂů ŶŝƚƌĂƚĞ o DĞƚĂů ŽdžŝĚĞ н copper carbonate copper(II) oxide 2
KdžLJŐĞŶ н EŝƚƌŽŐĞŶ
heat
ĚŝŽdžŝĚĞ 2Cu(NO ) (s) o 2CuO(s) + O (g) + 4NO (g)
2
2
3 2
copper nitrate
heat
2Ca(NO ) (s) o 2CaO(s) + O (g) + 4NO (g)
2
2
3 2
calcium nitrate
How is sodium hydroxide prepared
Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) can be prepared by heating a concentrated
solution of sodium carbonate and slakedlime. This process is called
causticising method.
heat
Na CO (aq) + Ca(OH) (aq) o CaCO (s)p + 2NaOH(aq)
3
2
3
2
sodium carbonate slakedlime calcium carbonate sodium hydroxide
How is ammonium hydroxide prepared
Ammonium hydroxide can be prepared by dissolving ammonia gas in
water.
NH (g) + H O(l) o NH OH(aq)
3
2
4
ammonia ammonium hydroxide
General Properties of Bases
Some typical properties of bases are given below:
Taste: Bases have bitter taste.
Touch: Bases have soapy (slippery) touch.
Nature: Strong bases (alkalis) have corrosive effect on the skin.
–
In aqueous solution: Bases give hydroxide ions (OH ) in aqueous
solutions. Strong bases (alkalis) when dissolved in water dissociate
completely, whereas weak bases in solution dissociate to a very small
extent.
–
+
NaOH(s) + H O o OH (aq) + Na (aq)
/ŶƐŽůƵďůĞ ĚƌLJ ďĂƐĞƐ ĚŽ ŶŽƚ ĂīĞĐƚ ƚŚĞ 2
ŝŶĚŝĐĂƚŽƌƐ͘ sodium hydroxide (excess) hydroxide ion sodium ion
ͻ [strong base (alkali)]
+
–
/Ĩ Ă ƐŽůƵƟŽŶ ƚƵƌŶƐ ƌĞĚ ůŝƚŵƵƐ ďůƵĞ ĂŶĚ NH OH + H O U NH (aq) + OH (aq)
4
2
4
ĐŽůŽƵƌůĞƐƐ ƉŚĞŶŽůƉŚƚŚĂůĞŝŶ ƚŽ ƉŝŶŬ͕ ŝƚ ammonium hydroxide ammonium ion hydroxide ion
ŝƐ Ă ďĂƐĞ Žƌ Ă ďĂƐŝĐ ƐŽůƵƟŽŶ͘ (weak base)
Action on indicators: Bases have the following effects on different
indicators:
Effect of a base on some indicators
Indicator Colour change
Red litmus Red to blue
Blue litmus No effect
/ŶƐŽůƵďůĞ ŵĞƚĂů ŚLJĚƌŽdžŝĚĞƐ Methyl orange Orange to yellow
ĚĞĐŽŵƉŽƐĞ ŽŶ ŚĞĂƟŶŐ͘
Phenolphthalein Colourless to pink
Turmeric solution Yellow to red
Action of heat: Some bases on heating lose water to form the
corresponding oxides. For example,
heat
Mg(OH) (s) o MgO(s) + H O(g)n
2
2
magnesium hydroxide magnesium oxide
heat
Cu(OH) (s) o CuO(s) + H O(g)n
2
2