Page 123 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 123
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding 111
The compounds having polar covalent bonds undergo ionisation
when dissolved in any polar solvent, such as water. Such polar compounds
in solutions produce free ions. For example, when hydrogen chloride (HCl)
+
–
is dissolved in water, it ionises to produce H O (hydronium ion) and Cl
3
(chloride ion).
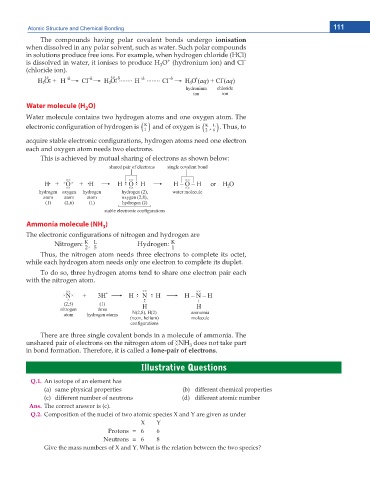
Water molecule (H O)
2
Water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The
K
electronic con guration of hydrogen is () and of oxygen is ( 2 K , L 6 ) . Thus, to
1
acquire stable electronic con gurations, hydrogen atoms need one electron
each and oxygen atom needs two electrons.
This is achieved by mutual sharing of electrons as shown below:
Ammonia molecule (NH )
3
The electronic con gurations of nitrogen and hydrogen are
Nitrogen: K L Hydrogen: K
,
2 5 1
Thus, the nitrogen atom needs three electrons to complete its octet,
while each hydrogen atom needs only one electron to complete its duplet.
To do so, three hydrogen atoms tend to share one electron pair each
with the nitrogen atom.
There are three single covalent bonds in a molecule of ammonia. The
×
unshared pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom of ×NH does not take part
3
in bond formation. Therefore, it is called a lone-pair of electrons.
Illustrative Questions
Q.1. An isotope of an element has
(a) same physical properties (b) different chemical properties
(c) different number of neutrons (d) different atomic number
Ans. The correct answer is (c).
Q.2. Composition of the nuclei of two atomic species X and Y are given as under
X Y
Protons = 6 6
Neutrons = 6 8
Give the mass numbers of X and Y. What is the relation between the two species?