Page 120 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 120
108 ICSE Chemistry – 9
Mg o Mg 2+ + 2e –
magnesium atom magnesium ion
(2,8,2) (2,8)
(neon con guration)
–
2Cl + 2e o 2Cl –
chlorine atom chloride ion
(2,8,7) (2,8,8)
(argon con guration)
–
2+
–
Mg 2+ + 2Cl o Mg (Cl ) o MgCl 2
2
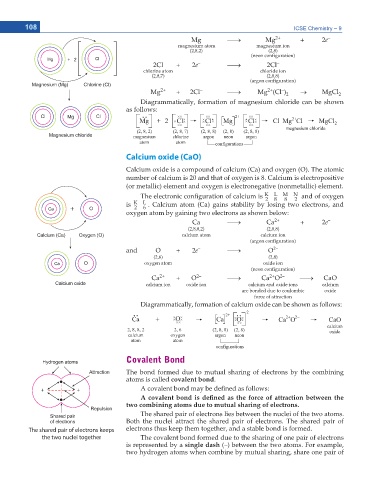
Diagrammatically, formation of magnesium chloride can be shown
as follows:
Calcium oxide (CaO)
Calcium oxide is a compound of calcium (Ca) and oxygen (O). The atomic
number of calcium is 20 and that of oxygen is 8. Calcium is electropositive
(or metallic) element and oxygen is electronegative (nonmetallic) element.
The electronic con guration of calcium is K L M N and of oxygen
2 8 8 2
is K L . Calcium atom (Ca) gains stability by losing two electrons, and
2 6
oxygen atom by gaining two electrons as shown below:
Ca o Ca 2+ + 2e –
(2,8,8,2) (2,8,8)
calcium atom calcium ion
(argon con guration)
–
and O + 2e o O 2–
(2,6) (2,8)
oxygen atom oxide ion
(neon con guration)
2+
2–
2–
Ca 2+ + O o Ca O o CaO
calcium ion oxide ion calcium and oxide ions calcium
are bonded due to coulombic oxide
force of attraction
Diagrammatically, formation of calcium oxide can be shown as follows:
Covalent Bond
The bond formed due to mutual sharing of electrons by the combining
atoms is called covalent bond.
A covalent bond may be de ned as follows:
# EQXCNGPV DQPF KU FGſPGF CU VJG HQTEG QH CVVTCEVKQP DGVYGGP VJG
two combining atoms due to mutual sharing of electrons.
The shared pair of electrons lies between the nuclei of the two atoms.
Both the nuclei attract the shared pair of electrons. The shared pair of
electrons thus keep them together, and a stable bond is formed.
The shared pair of electrons keeps
the two nuclei together The covalent bond formed due to the sharing of one pair of electrons
is represented by a single dash (–) between the two atoms. For example,
two hydrogen atoms when combine by mutual sharing, share one pair of