Page 121 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 121
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding 109
electrons between them. So, the covalent bond formed between the two
hydrogen atoms (H) is shown as a dash, (–) viz,
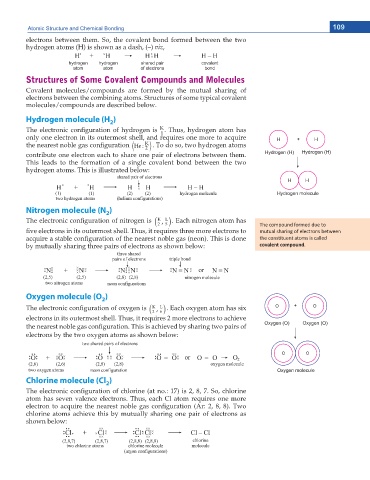
Structures of Some Covalent Compounds and Molecules
Covalent molecules/compounds are formed by the mutual sharing of
electrons between the combining atoms. Structures of some typical covalent
molecules/compounds are described below.
Hydrogen molecule (H )
2
K
The electronic con guration of hydrogen is . Thus, hydrogen atom has
1
only one electron in its outermost shell, and requires one more to acquire
(
the nearest noble gas con guration He : K ) . To do so, two hydrogen atoms
2
contribute one electron each to share one pair of electrons between them.
This leads to the formation of a single covalent bond between the two
hydrogen atoms. This is illustrated below:
Nitrogen molecule (N )
2
The electronic con guration of nitrogen is K , L ) . Each nitrogen atom has
( 2 5 dŚĞ ĐŽŵƉŽƵŶĚ ĨŽƌŵĞĚ ĚƵĞ ƚŽ
ve electrons in its outermost shell. Thus, it requires three more electrons to ŵƵƚƵĂů ƐŚĂƌŝŶŐ ŽĨ ĞůĞĐƚƌŽŶƐ ďĞƚǁĞĞŶ
acquire a stable con guration of the nearest noble gas (neon). This is done ƚŚĞ ĐŽŶƐƟƚƵĞŶƚ ĂƚŽŵƐ ŝƐ ĐĂůůĞĚ
by mutually sharing three pairs of electrons as shown below: covalent compound.
Oxygen molecule (O )
2
The electronic con guration of oxygen is K , L ) . Each oxygen atom has six
( 2 6
electrons in its outermost shell. Thus, it requires 2 more electrons to achieve
the nearest noble gas con guration. This is achieved by sharing two pairs of
electrons by the two oxygen atoms as shown below:
Chlorine molecule (Cl )
2
The electronic con guration of chlorine (at no.: 17) is 2, 8, 7. So, chlorine
atom has seven valence electrons. Thus, each Cl atom requires one more
electron to acquire the nearest noble gas con guration (Ar: 2, 8, 8). Two
chlorine atoms achieve this by mutually sharing one pair of electrons as
shown below: