Page 125 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 125
Analytical Chemistry 111
Let us say it Again
Qualitative analysis. Identifying the constituents of a substance or a mixture of substances by physical and chemical
methods is called qualitative analysis.
Chemical tests. These are of two types.
Dry tests
Wet tests
Dry tests. These tests are conducted on dry sample and include
Effect of heat
Colour and smell of the gas/vapour evolved
Wet tests. The chemical tests carried out on the solution of the given salt or a mixture of salts are called wet tests.
Colour of the salts. The colour of salt is mainly due to the nature of the cation present in it. However, certain oxoanions
of transition metals impart characteristic colours to the salts.
Ions which form colourless salts are
3+
2+
2+
+
2+
+
2+
+
Cations: NH , Na , K , Ca , Mg , Al , Pb , Zn
4
–
–
Anions: CO 3 2– , HCO , SO 4 2– , Cl , CH COO –
3
3
Ions which form coloured salts are
2+
2+
3+
Cations: Cu (blue), Fe (light green), Fe (yellow-brown),
2+
3+
2+
2+
Ni (green), Cr (bluish-green), Mn (pink), CO (violet-pink)
–
Anions: MnO (purple), CrO 2– (yellow), Cr O 2– (orange)
4 4 2 7
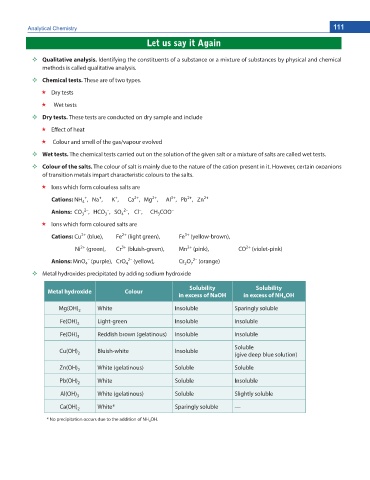
Metal hydroxides precipitated by adding sodium hydroxide
Solubility Solubility
Metal hydroxide Colour
in excess of NaOH in excess of NH OH
4
Mg(OH) 2 White Insoluble Sparingly soluble
Fe(OH) Light-green Insoluble Insoluble
2
Fe(OH) 3 Reddish brown (gelatinous) Insoluble Insoluble
Soluble
Cu(OH) Bluish-white Insoluble
2 (give deep blue solution)
Zn(OH) 2 White (gelatinous) Soluble Soluble
Pb(OH) White Soluble Insoluble
2
Al(OH) 3 White (gelatinous) Soluble Slightly soluble
Ca(OH) White* Sparingly soluble —
2
* No precipitation occurs due to the addition of NH OH.
4