Page 122 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 122
108 ICSE Chemistry – 10
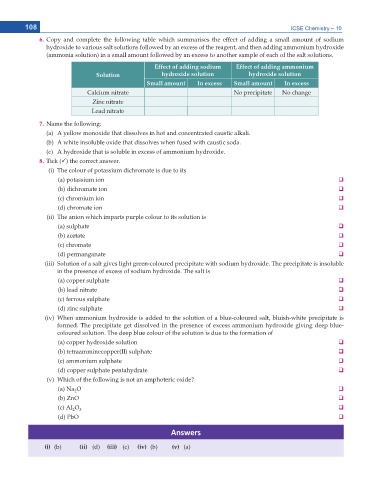
6. Copy and complete the following table which summarises the effect of adding a small amount of sodium
hydroxide to various salt solutions followed by an excess of the reagent, and then adding ammonium hydroxide
(ammonia solution) in a small amount followed by an excess to another sample of each of the salt solutions.
Effect of adding sodium Effect of adding ammonium
Solution hydroxide solution hydroxide solution
Small amount In excess Small amount In excess
Calcium nitrate No precipitate No change
Zinc nitrate
Lead nitrate
7. Name the following:
(a) A yellow monoxide that dissolves in hot and concentrated caustic alkali.
(b) A white insoluble oxide that dissolves when fused with caustic soda.
(c) A hydroxide that is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide.
8. Tick (9) the correct answer.
(i) The colour of potassium dichromate is due to its
(a) potassium ion
(b) dichromate ion
(c) chromium ion
(d) chromate ion
(ii) The anion which imparts purple colour to its solution is
(a) sulphate
(b) acetate
(c) chromate
(d) permanganate
(iii) Solution of a salt gives light green-coloured precipitate with sodium hydroxide. The precipitate is insoluble
in the presence of excess of sodium hydroxide. The salt is
(a) copper sulphate
(b) lead nitrate
(c) ferrous sulphate
(d) zinc sulphate
(iv) When ammonium hydroxide is added to the solution of a blue-coloured salt, bluish-white precipitate is
formed. The precipitate get dissolved in the presence of excess ammonium hydroxide giving deep blue-
coloured solution. The deep blue colour of the solution is due to the formation of
(a) copper hydroxide solution
(b) tetraamminecopper(II) sulphate
(c) ammonium sulphate
(d) copper sulphate pentahydrate
(v) Which of the following is not an amphoteric oxide?
(a) Na O
2
(b) ZnO
(c) Al O
2
3
(d) PbO
ŶƐǁĞƌƐ
(i) (b) (ii) (d) (iii) (c) (iv) (b) (v) (a)