Page 108 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 108
96 ICSE Chemistry – 9
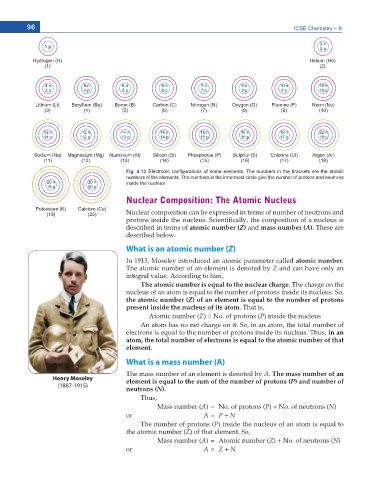
Fig. 4.13 Electronic con¿gurations of some elements. The numbers in the brackets are the atomic
numbers of the elements. The numbers in the innermost circle give the number of protons and neutrons
inside the nucleus
Nuclear Composition: The Atomic Nucleus
Nuclear composition can be expressed in terms of number of neutrons and
protons inside the nucleus. Scienti cally, the composition of a nucleus is
described in terms of atomic number (Z) and mass number (A). These are
described below.
What is an atomic number (Z)
In 1913, Moseley introduced an atomic parameter called atomic number.
The atomic number of an element is denoted by Z and can have only an
integral value. According to him,
The atomic number is equal to the nuclear charge. The charge on the
nucleus of an atom is equal to the number of protons inside its nucleus. So,
the atomic number (Z) of an element is equal to the number of protons
present inside the nucleus of its atom. That is,
Atomic number (Z) = No. of protons (P) inside the nucleus
An atom has no net charge on it. So, in an atom, the total number of
electrons is equal to the number of protons inside its nucleus. Thus, in an
atom, the total number of electrons is equal to the atomic number of that
element.
What is a mass number (A)
The mass number of an element is denoted by A. The mass number of an
Henry Moseley element is equal to the sum of the number of protons (P) and number of
(1887-1915)
neutrons (N).
Thus,
Mass number (A) = No. of protons (P) + No. of neutrons (N)
or A = P + N
The number of protons (P) inside the nucleus of an atom is equal to
the atomic number (Z) of that element. So,
Mass number (A) = Atomic number (Z) + No. of neutrons (N)
or A = Z + N