Page 90 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 90
78 ICSE Chemistry – 9
What are the common uses of water
Various common uses of water are given below:
For drinking purposes
For washing, bathing, cooking, etc.
For construction purposes
For the generation of steam for industrial use and electricity generation
For generating hydroelectricity
For the manufacture of hydrogen, oxygen and water gas
As a solvent
For irrigation purposes
What are the characteristics of drinking water
(or potable water)
Following are the characteristics of drinking water:
Drinking water should be colourless and odourless.
It should also be free from;
any suspended impurities
any harmful germs
large quantity of salts
any harmful salt, such as nitrates, cyanides and urea.
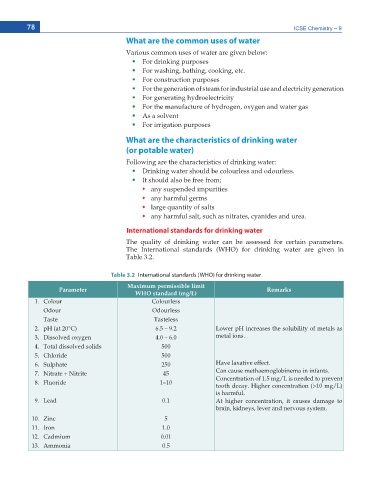
International standards for drinking water
The quality of drinking water can be assessed for certain parameters.
The International standards (WHO) for drinking water are given in
Table 3.2.
Table 3.2 International standards (WHO) for drinking water
Maximum permissible limit
Parameter Remarks
WHO standard (mg/L)
1. Colour Colourless
Odour Odourless
Taste Tasteless
2. pH (at 20°C) 6.5 – 9.2 Lower pH increases the solubility of metals as
3. Dissolved oxygen 4.0 – 6.0 metal ions.
4. Total dissolved solids 500
5. Chloride 500
6. Sulphate 250 Have laxative effect.
7. Nitrate + Nitrite 45 Can cause methaemoglobinema in infants.
8. Fluoride 1–10 Concentration of 1.5 mg/L is needed to prevent
tooth decay. Higher concentration (>10 mg/L)
is harmful.
9. Lead 0.1 At higher concentration, it causes damage to
brain, kidneys, lever and nervous system.
10. Zinc 5
11. Iron 1.0
12. Cadmium 0.01
13. Ammonia 0.5