Page 194 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 194
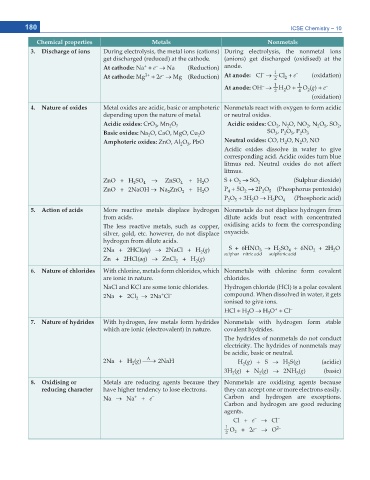
180 ICSE Chemistry – 10
Chemical properties Metals Nonmetals
3. Discharge of ions During electrolysis, the metal ions (cations) During electrolysis, the nonmetal ions
get discharged (reduced) at the cathode. (anions) get discharged (oxidised) at the
+
–
At cathode: Na + e o Na (Reduction) anode.
1
–
–
2+
At cathode: Mg + 2e o Mg (Reduction) At anode: Cl o Cl + e – (oxidation)
2
2
1
1
–
At anode: OH o H O + O (g) + e –
2
2
2
4
(oxidation)
4. Nature of oxides Metal oxides are acidic, basic or amphoteric Nonmetals react with oxygen to form acidic
depending upon the nature of metal. or neutral oxides.
Acidic oxides: CrO , Mn O 7 Acidic oxides: CO , N O, NO , N O , SO ,
5
2
2
2
2
3
2
2
Basic oxides: Na O, CaO, MgO, Cu O SO , P O , P O 3
2
3
2
5
2
2
Amphoteric oxides: ZnO, Al O , PbO Neutral oxides: CO, H O, N O, NO
2
2
2
3
Acidic oxides dissolve in water to give
corresponding acid. Acidic oxides turn blue
litmus red. Neutral oxides do not affect
litmus.
ZnO + H SO o ZnSO + H O S + O o SO 2 (Sulphur dioxide)
2
4
4
2
2
ZnO + 2NaOH o Na ZnO + H O P + 5O o 2P O (Phosphorus pentoxide)
4
5
2
2
2
2
2
P O + 3H O o H PO 4 (Phosphoric acid)
2
3
2
5
5. Action of acids More reactive metals displace hydrogen Nonmetals do not displace hydrogen from
from acids. dilute acids but react with concentrated
The less reactive metals, such as copper, oxidising acids to form the corresponding
silver, gold, etc. however, do not displace oxyacids.
hydrogen from dilute acids.
2Na + 2HCl(aq) o 2NaCl + H (g) S + 6HNO o H SO + 6NO + 2H O
3
2
4
2
2
2
Zn + 2HCl(aq) o ZnCl + H (g) sulphur nitric acid sulphuric acid
2
2
6. Nature of chlorides With chlorine, metals form chlorides, which Nonmetals with chlorine form covalent
are ionic in nature. chlorides.
NaCl and KCl are some ionic chlorides. Hydrogen chloride (HCl) is a polar covalent
+
2Na + 2Cl o 2Na Cl – compound. When dissolved in water, it gets
2
ionised to give ions.
+
HCl + H O o H O + Cl –
3
2
7. Nature of hydrides With hydrogen, few metals form hydrides Nonmetals with hydrogen form stable
which are ionic (electrovalent) in nature. covalent hydrides.
The hydrides of nonmetals do not conduct
electricity. The hydrides of nonmetals may
be acidic, basic or neutral.
'
2Na + H (g) o 2NaH H (g) + S o H S(g) (acidic)
2
2
2
3H (g) + N (g) o 2NH (g) (basic)
3
2
2
8. Oxidising or Metals are reducing agents because they Nonmetals are oxidising agents because
reducing character have higher tendency to lose electrons. they can accept one or more electrons easily.
+
Na o Na + e – Carbon and hydrogen are exceptions.
Carbon and hydrogen are good reducing
agents.
–
Cl + e o Cl –
1 O + 2e o O 2–
–
2 2