Page 199 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 199
Metallurgy 185
Concentration of the Ore
How is an ore concentrated
Ores usually contain unwanted earthly materials called gangue. The
gangue must be removed before the ore is processed further. The removal
of unwanted earthly materials from an ore is called concentration of ore.
Concentration of an ore is also called dressing of ore.
Based on the nature of gangue and the ore, the following methods are
generally used for the concentration of ores:
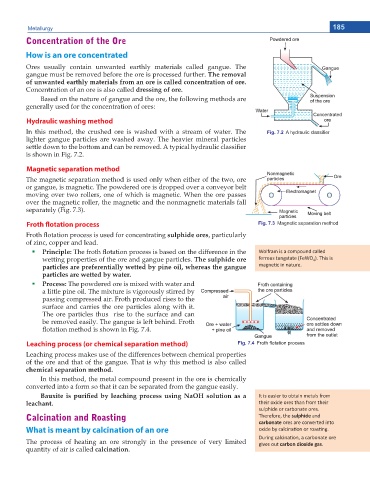
Hydraulic washing method
In this method, the crushed ore is washed with a stream of water. The Fig. 7.2 $ K\GUDXOLF FODVVL¿HU
lighter gangue particles are washed away. The heavier mineral particles
UGVVNG FQYP VQ VJG DQVVQO CPF ECP DG TGOQXGF # V[RKECN J[FTCWNKE ENCUUKſGT
is shown in Fig. 7.2.
Magnetic separation method
The magnetic separation method is used only when either of the two, ore
or gangue, is magnetic. The powdered ore is dropped over a conveyor belt
moving over two rollers, one of which is magnetic. When the ore passes
over the magnetic roller, the magnetic and the nonmagnetic materials fall
separately (Fig. 7.3).
Froth flotation process Fig. 7.3 Magnetic separation method
(TQVJ ƀQVCVKQP RTQEGUU KU WUGF HQT EQPEGPVTCVKPI sulphide ores, particularly
of zinc, copper and lead.
Principle: 6JG HTQVJ ƀQVCVKQP RTQEGUU KU DCUGF QP VJG FKHHGTGPEG KP VJG tŽůĨƌĂŵ ŝƐ Ă ĐŽŵƉŽƵŶĚ ĐĂůůĞĚ
wetting properties of the ore and gangue particles. The sulphide ore ĨĞƌƌŽƵƐ ƚƵŶŐƐƚĂƚĞ ;&ĞtK Ϳ͘ dŚŝƐ ŝƐ
ϰ
particles are preferentially wetted by pine oil, whereas the gangue ŵĂŐŶĞƟĐ ŝŶ ŶĂƚƵƌĞ͘
particles are wetted by water.
Process: The powdered ore is mixed with water and
a little pine oil. The mixture is vigorously stirred by
passing compressed air. Froth produced rises to the
surface and carries the ore particles along with it.
The ore particles thus rise to the surface and can
be removed easily. The gangue is left behind. Froth
ƀQVCVKQP OGVJQF KU UJQYP KP (KI
Leaching process (or chemical separation method) Fig. 7.4 )URWK ÀRWDWLRQ SURFHVV
Leaching process makes use of the differences between chemical properties
of the ore and that of the gangue. That is why this method is also called
chemical separation method.
In this method, the metal compound present in the ore is chemically
converted into a form so that it can be separated from the gangue easily.
$CWZKVG KU RWTKſGF D[ NGCEJKPI RTQEGUU WUKPI 0C1* UQNWVKQP CU C /ƚ ŝƐ ĞĂƐŝĞƌ ƚŽ ŽďƚĂŝŶ ŵĞƚĂůƐ ĨƌŽŵ
leachant. ƚŚĞŝƌ ŽdžŝĚĞ ŽƌĞƐ ƚŚĂŶ ĨƌŽŵ ƚŚĞŝƌ
ƐƵůƉŚŝĚĞ Žƌ ĐĂƌďŽŶĂƚĞ ŽƌĞƐ͘
Calcination and Roasting dŚĞƌĞĨŽƌĞ͕ ƚŚĞ sulphide ĂŶĚ
carbonate ŽƌĞƐ ĂƌĞ ĐŽŶǀĞƌƚĞĚ ŝŶƚŽ
What is meant by calcination of an ore ŽdžŝĚĞ ďLJ ĐĂůĐŝŶĂƟŽŶ Žƌ ƌŽĂƐƟŶŐ͘
ƵƌŝŶŐ ĐĂůĐŝŶĂƟŽŶ͕ Ă ĐĂƌďŽŶĂƚĞ ŽƌĞ
The process of heating an ore strongly in the presence of very limited ŐŝǀĞƐ ŽƵƚ carbon dioxide gas͘
quantity of air is called calcination.