Page 206 - Chemistry ICSE Class X
P. 206
192 ICSE Chemistry – 10
Electrolyte. A molten mixture of alumina (Al O ) (20%), cryolite
2
3
(Na AlF CPF ƀWQTURCT %C( ) (20%) is used as the electrolyte.
6
2
3
Cryolite (Na AlF ) is added to alumina to:
6
3
Lower the melting temperature of alumina
Make the electrolyte a good conductor of electricity.
Process. When electric current is passed through the electrolyte,
aluminium metal is obtained at the cathode, while oxygen gas is
liberated at the anode. During electrolysis, when the concentration of
alumina falls below a certain level, the indicator bulb starts glowing.
To make up for the loss of alumina in the electrolyte, more alumina
is added to it.
The following reactions take place during the electrolysis of alumina
(dissolved in cryolite):
Na AlF o 3NaF + AlF 3
3
6
AlF U Al 3+ + 3F –
3
–
3+
At cathode: Al + 3e o Al (Reduction)
from the aluminium metal
electrolyte (liberated at the cathode)
3
–
–
At anode: 1 2 Al O + 3F o AlF + O + 3e (Oxidation)
2
2
3
3
4
from the
electrolyte
The oxygen liberated at the anode either goes out as oxygen gas or
reacts with carbon of the anode to form carbon dioxide (CO ).
2
C(s) + O (g) o CO (g)
2
2
from anode
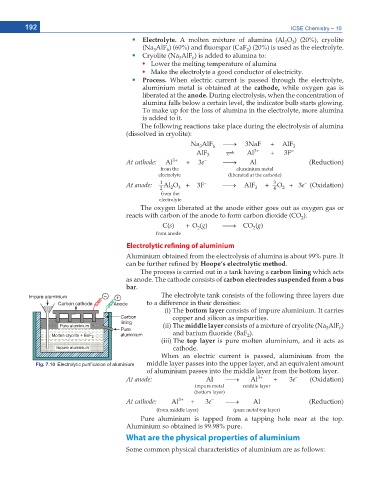
Electrolytic refining of aluminium
Aluminium obtained from the electrolysis of alumina is about 99% pure. It
ECP DG HWTVJGT TGſPGF D[ Hoope’s electrolytic method.
The process is carried out in a tank having a carbon lining which acts
as anode. The cathode consists of carbon electrodes suspended from a bus
bar.
The electrolyte tank consists of the following three layers due
to a difference in their densities:
(i) The bottom layer consists of impure aluminium. It carries
copper and silicon as impurities.
(ii) The middle layer consists of a mixture of cryolite (Na AlF )
3
6
CPF DCTKWO ƀWQTKFG $C( ).
2
(iii) The top layer is pure molten aluminium, and it acts as
cathode.
When an electric current is passed, aluminium from the
Fig. 7.10 (OHFWURO\WLF SXUL¿FDWLRQ RI DOXPLQLXP middle layer passes into the upper layer, and an equivalent amount
of aluminium passes into the middle layer from the bottom layer.
At anode: Al o Al 3+ + 3e – (Oxidation)
impure metal middle layer
(bottom layer)
–
3+
At cathode: Al + 3e o Al (Reduction)
(from middle layer) (pure metal top layer)
Pure aluminium is tapped from a tapping hole near at the top.
Aluminium so obtained is 99.98% pure.
What are the physical properties of aluminium
Some common physical characteristics of aluminium are as follows: