Page 114 - Chemistry ICSE Class IX
P. 114
102 ICSE Chemistry – 9
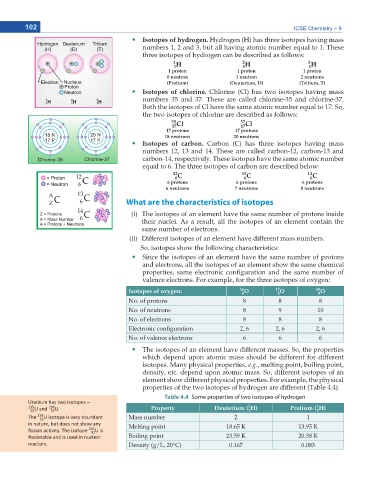
Isotopes of hydrogen. Hydrogen (H) has three isotopes having mass
numbers 1, 2 and 3, but all having atomic number equal to 1. These
three isotopes of hydrogen can be described as follows:
1 1 H 2 1 H 3 1 H
1 proton 1 proton 1 proton
0 neutron 1 neutron 2 neutrons
(Protium) (Deuterium, D) (Tritium, T)
Isotopes of chlorine. Chlorine (Cl) has two isotopes having mass
numbers 35 and 37. These are called chlorine-35 and chlorine-37.
Both the isotopes of Cl have the same atomic number equal to 17. So,
the two isotopes of chlorine are described as follows:
35 Cl 37 Cl
17
17
17 protons 17 protons
18 neutrons 20 neutrons
Isotopes of carbon. Carbon (C) has three isotopes having mass
numbers 12, 13 and 14. These are called carbon-12, carbon-13 and
carbon-14, respectively. These isotopes have the same atomic number
equal to 6. The three isotopes of carbon are described below:
12 6 C 13 6 C 14 6 C
6 protons 6 protons 6 protons
6 neutrons 7 neutrons 8 neutrons
What are the characteristics of isotopes
(i) The isotopes of an element have the same number of protons inside
their nuclei. As a result, all the isotopes of an element contain the
same number of electrons.
(ii) Different isotopes of an element have different mass numbers.
So, isotopes show the following characteristics:
Since the isotopes of an element have the same number of protons
and electrons, all the isotopes of an element show the same chemical
properties, same electronic con guration and the same number of
valence electrons. For example, for the three isotopes of oxygen:
Isotopes of oxygen: 16 8 O 17 8 O 18 8 O
No. of protons 8 8 8
No. of neutrons 8 9 10
No. of electrons 8 8 8
Electronic con guration 2, 6 2, 6 2, 6
No. of valence electrons 6 6 6
The isotopes of an element have different masses. So, the properties
which depend upon atomic mass should be different for different
isotopes. Many physical properties, e.g., melting point, boiling point,
density, etc. depend upon atomic mass. So, different isotopes of an
element show different physical properties. For example, the physical
properties of the two isotopes of hydrogen are different (Table 4.4).
Table 4.4 Some properties of two isotopes of hydrogen
hƌĂŶŝƵŵ ŚĂƐ ƚǁŽ ŝƐŽƚŽƉĞƐ ʹ
1
2
Ϯϯϱ h ĂŶĚ Ϯϯϴ h͘ Property Deuterium ( H) Protium ( H)
ϵϮ ϵϮ 1 1
dŚĞ Ϯϯϴ h ŝƐŽƚŽƉĞ ŝƐ ǀĞƌLJ ĂďƵŶĚĂŶƚ Mass number 2 1
ϵϮ
ŝŶ ŶĂƚƵƌĞ͕ ďƵƚ ĚŽĞƐ ŶŽƚ ƐŚŽǁ ĂŶLJ Melting point 18.65 K 13.95 K
ĮƐƐŝŽŶ ĂĐƟǀŝƚLJ͘ dŚĞ ŝƐŽƚŽƉĞ Ϯϯϱ h ŝƐ
ϵϮ
ĮƐƐŝŽŶĂďůĞ ĂŶĚ ŝƐ ƵƐĞĚ ŝŶ ŶƵĐůĞĂƌ Boiling point 23.59 K 20.38 K
ƌĞĂĐƚŽƌƐ͘ Density (g/L, 20°C) 0.167 0.083